/regions/physiography
Physiography
Koodam – Breaking hierarchy, building democracy - Paper published in Integral Leadership Review
Posted on 08 Jan, 2012 03:59 PMThe paper published in the Integral Leadership Review argues that hierarchy and bureaucracy are two of the most common features of governance systems that play a determining role in shaping the organisational culture, systemic re
Examining the storm protection services of mangroves of Orissa during the 1999 cyclone – A special article in EPW
Posted on 06 Jan, 2012 11:03 PMThese ecosystems provide a bunch of direct and indirect services to humankind. This special article in Economic and Political Weekly (EPW) by Saudamini Das examines whether the mangrove forests in Kendrapada district of Orissa played any protective role during the severe cyclone that hit the state in October 1999.
Floods in Orissa: No lessons learnt – An article in EPW
Posted on 06 Jan, 2012 02:26 PMThis article by Kishore C Samal in the Economic and Political Weekly (EPW) discusses how in the natural disater prone state of Orissa the authorities have not been able to draw up an effective disaster management plan and politicians continue to play politics with relief works. It argues that for dealing with these disasters and the relief and rehabilitation work that follows what is needed is the participation of the local community and functionaries of panchayati raj institutions, and coordination with national and international bodies.
Big dams and protests in India: A study of Hirakud dam – An article in EPW
Posted on 06 Jan, 2012 12:29 PMIt is evident that the domestic resistance to the project was variously compromised by nationalist rhetoric, imperatives of state development and absence of transnational support. The Hirakud dam project has failed on all of its objectives – flood management, hydropower production, irrigation and navigation. Its socio-economic impact has been devastating.
Living rivers, dying rivers: Bagmati river in Nepal
Posted on 05 Jan, 2012 06:07 PMBagmati river in Kathmandu: From holy river to unthinkable flowing filth
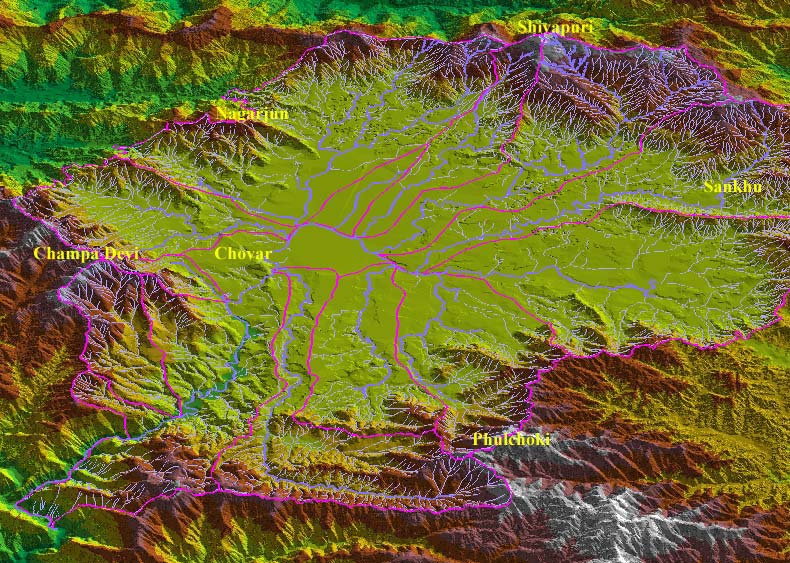
Ajaya Dixit initiated his presentation with a general account of how rivers shape the landscape and how riverine ecosystems have nurtured society and kept civilisations vibrant, cultured and creative. Dixit went on to discuss the basin characteristics of the Bagmati, a tributary of the Kosi that rises in the Shivapuri hills, north of the Kathmandu valley. Around fifteen percent of the basin area (3700 sqkm) lies in Nepal, while the remaining is in India. The average annual rainfall in the basin is 1400 mm and is more than 2000 mm in the hills. Bagmati is a seasonal river with rainfall and springs as its main source. Its mean flow is 15.6 cubic metre/second and low flow is 0.15 cubic metre/second in April.
Kathmandu lies in the Upper Bagmati basin and studies suggest that an ancient lake called the Paleo-Kathmandu lay within the Kathmandu valley as a lacustrine formation. Early settlers lived in lower slopes and used springs and river in the upper reaches. When they moved to the valley floor, they built dongia dharas, which are stone water spouts fed by the unconfined aquifers and delivered water through surface channels. Even today, dongia dharas dated back to 1500 years exist. The state built canals (raj kulo) tapped the upper stretches of the rivers close to the mountains. Rivers and irrigation helped recharge aquifers and ponds.
However, rising urbanisation has damaged these ancient artifacts. Over the last sixty years Kathmandu has expanded massively and its population has increased from 0.41 million in 1951 to 2.6 million in 2011. The city has a huge transient population aside from this, reducing it to a concrete nightmare. Seismologists suggest that Kathmandu is a rubble city in the making. Though the Bagmati river flow has not changed significantly in the last seventy years, the character of the river has been transformed significantly during the period 1970 to 1990. The river has been canalised while the dumping of the city’s garbage into it continues. Dixit identified a plethora of problems faced by the river such as upstream water diversion for drinking water needs, disposal of untreated liquid waste, disposal of solid waste, river jacketing for roads and commercial activities, sand mining and physical encroachment.
The state of the river is an outcome of the current approach to waste management particularly liquid waste management. Three types of waste water namely yellow water flux, grey water and yellow black flux are being generated and flowing water is being used as a vehicle to dispose these. The idea of a water based disposal system e.g. flush toilet embedded in Victorian engineering has led to a technological lock-in with the result that the notion of a natural hydrological cycle has undergone a fundamental transformation.
All the same, the bulk of the load in the river is biological though there are some factories releasing effluents. In the last 20 years some of them have been closed or relocated and the river now stands a chance of being salvaged.

Managing natural resources through simple and appropriate technological interventions for sustainable mountain development - Current Science (2011)
Posted on 30 Dec, 2011 10:07 AMThe initiative on management of natural resources through appropriate interventions aimed at:
Investigation and assessment report: Arsenic in drinking water sources and related problems of Ballia district of Uttar Pradesh
Posted on 28 Dec, 2011 11:03 AMFollowing media reports about arsenic contamination in Ballia, and a complaint addressed by the people of Ballia to the Ministry of Rural Development, a National Level Monitor was requested to enquire into the issue of water quality.
Agriculture, food security and nutrition in Vidarbha: Household level analysis – A special article in EPW
Posted on 27 Dec, 2011 09:43 AMUsing the data generated from a baseline survey on a sample of 6,990 households covering six districts, this paper attempts to assess the relationships between agriculture, food security and nutrition for children, adolescents and married women of reproductive age.
Confessions of an OD boy: The need to achieve a sustainable open defacation free intervention
Posted on 24 Dec, 2011 07:58 PMAuthor: Mohanasundar Radhakrishnan
The impacts of water infrastructure and climate change on the hydrology of the Upper Ganges river basin – A research report by IWMI
Posted on 18 Dec, 2011 07:03 PM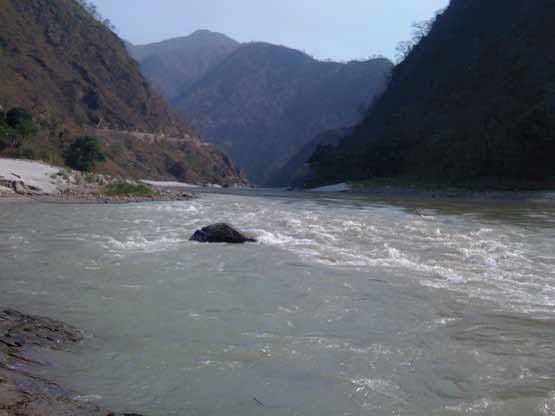 The Ganges river system originates in the Central Himalayas, and extends into the alluvial Gangetic Plains and drains into the Indian Ocean at the Bay of Bengal. In the upstream mountainous regions, hydropower is the main focus of development with mega and micro projects either under construction or being planned in both Nepal and India.
The Ganges river system originates in the Central Himalayas, and extends into the alluvial Gangetic Plains and drains into the Indian Ocean at the Bay of Bengal. In the upstream mountainous regions, hydropower is the main focus of development with mega and micro projects either under construction or being planned in both Nepal and India.
After the main river channel reaches the plains, it is highly regulated with dams, barrages and associated irrigation canals. All this infrastructure development and abstractions affects the river’s flow regime and reduces flows, which, in turn, impacts downstream water availability, water quality and riverine ecosystems. Furthermore, there are concerns that climate change is likely to exacerbate the water scarcity problem in the Ganges Basin. Therefore, modeling the hydrology of the basin is critical for estimation, planning and management of current and future water resources.