The Central Rural Sanitation Programme, which was started in 1986, was one of India’s first efforts to provide safe sanitation in rural areas. This programme focussed mainly on providing subsidies to people to construct sanitation facilities. However, a study done by the government in 1996-97 showed that it was more important to raise awareness about sanitation as a whole rather than to just provide subsidies for construction. This understanding marked the first shift in the programme. In 1999, a restructured Total Sanitation Campaign (TSC) was initiated to create supply-led sanitation by promoting local sanitary marts and a range of technological options.
The rural sanitation campaign has the following as its objectives:
- Accelerate sanitation coverage in rural areas.
- Generate a push from the people to get facilities rather than expect the Government to do it (demand-led promotion).
- Focus on intensive education and awareness campaigns to ensure that people understand the need for safe sanitation.
- Take the scheme beyond rural households to rural schools and nursery schools. Here again, the emphasis was placed on promoting good hygiene practices.
- Promote cost-effective and appropriate technologies.
- Through all the above, improve the health and quality of life in rural areas.
The last modification of the scheme happened in 2012. It was restructured and renamed as the Nirmal Bharat Abhiyan. With an intent to transform India to "Nirmal Bharat", the scheme's revised target for reaching total sanitation was changed from 2012 to 2022.
Understanding rural sanitation data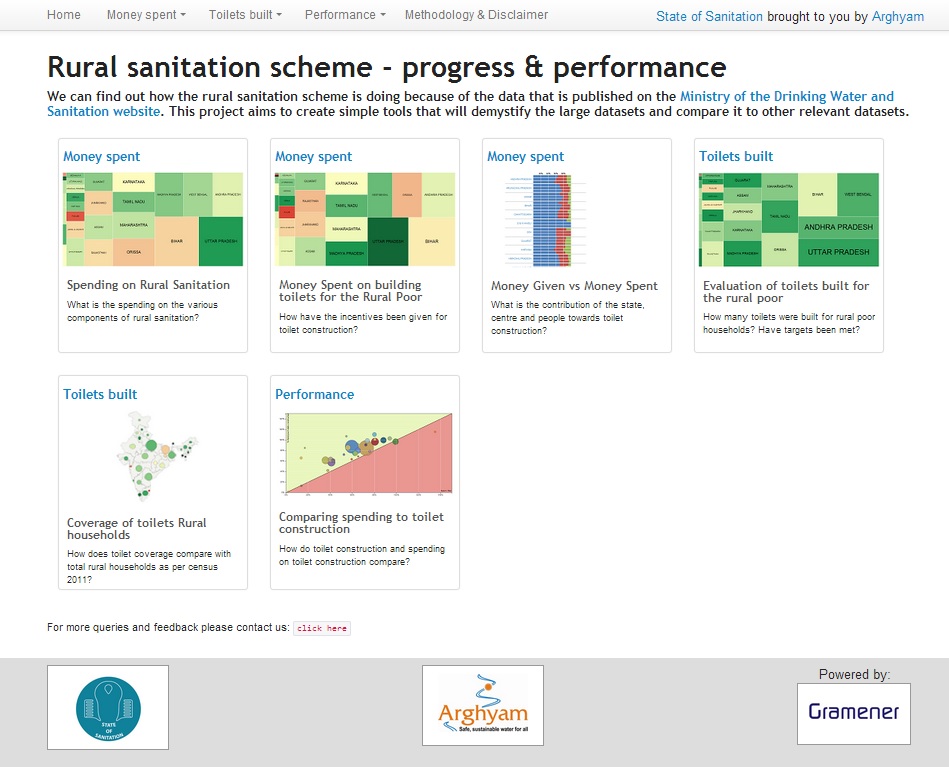
The Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation publishes data related to the rural sanitation scheme on its website. The State of Sanitation Project is an effort to create simple tools that will demystify large datasets and also compare it to other relevant datasets.
View the State of sanitation in India - Data visualisation tool.
From outlays to outcomes: understanding the status of rural sanitation data
The census 2011 data on rural sanitation coverage was a reality check to the existing understanding that the government’s efforts at rural sanitation were moving rapidly towards achieving universal coverage.
Below are some key lessons that emerged:
- A difference in the total number of rural households as counted by the census 2011 and the government scheme – while in 2001, the difference was 0.14 lakhs, in 2011, the difference had grown to 884.03 lakhs.
- A huge difference in the number of rural households with toilets. According to census 2011 data, only 30.7% of rural households had access to toilets in 2011. According to rural sanitation scheme data the number was considerably larger at 79.9%.
Some of these differences can be accounted for by the fact that the sanitation scheme achievement number was calculated on household numbers that were lesser than the 2011 household number. When corrected for this, the total achievement fell to 65.7 percent, which was still significantly higher than the number reported by the census 2011.
Based on these calculations India will have to spend anywhere between 9 – 19 times of its expenditure up to 2011 (Rs. 6140 crore) in order to achieve universal coverage of household toilets – which is just one component of the government scheme.
Download and read the entire study: From outlays to outcomes - The state of rural sanitation data in India - A report by Accountability Initiative and Arghyam (2013).
Download rural sanitation fact sheets for all states of India.
Accountability Initiative, Centre for Policy Research carried out the research for the State of Sanitation Project. Arghyam supported the effort.
About the State of Sanitation Project
The goal of the State of Sanitation project is to understand the success of the government’s rural sanitation scheme from the lenses of coverage, equity, accountability, efficiency and health.
Open defecation in rural India remains a problem that perplexes policy makers and civil society alike. India has the largest number of people who practice open defecation (626 million) and the most number of child deaths due to poor water, sanitation and hygiene conditions compared to the rest of the world.
While access to toilets is by itself an important aspect that needs to be understood, it is not enough to reach the goal of total sanitation. Indeed, India’s rural sanitation scheme which was devised in 1986 and restructured in 2012 as the Nirmal Bharat Abhiyan (NBA) acknowledges this. Its goal is not only universal toilet coverage by 2022, but also improving health and providing privacy and dignity to women, with the overall goal of improving the quality of life of people living in rural areas.
Aims of the State of Sanitation project: Multiple agencies have assessed the status of the rural sanitation programme and have quantified its benefits over time. However, there have been few attempts to provide an online, concurrent monitoring mechanism to track the status of both the implementation of the scheme and the larger benefits from the scheme.
To this end, the project will:
- Design monitoring tools – this will include:
-
- Online tools that help demystify government data and provide overlays between multiple data sets relevant to sanitation. These tools will be opened up to civil society and provide context to the large data sets.
- Participatory assessment tools that will attempt to qualify how the scheme is working and issues in implementation, usage and achievement of the rural sanitation scheme’s goals.
-
- Identify best practices and gaps in implementation – this will include:
-
- Ground verification of best practices and issues.
- Focussed efforts to document good practices and problems.
-
For more queries or feedback, please contact us.
/topics/rural-sanitation