/topics/international-issues
International Issues
Implementation of the interlinking of rivers project (ILRP): Bangladesh raises concerns
Posted on 12 Mar, 2012 11:50 AMAuthor : Md. Khalequzzaman, P.D.
Koodam – Breaking hierarchy, building democracy - Paper published in Integral Leadership Review
Posted on 08 Jan, 2012 03:59 PMThe paper published in the Integral Leadership Review argues that hierarchy and bureaucracy are two of the most common features of governance systems that play a determining role in shaping the organisational culture, systemic re
Living rivers, dying rivers: Bagmati river in Nepal
Posted on 05 Jan, 2012 06:07 PMBagmati river in Kathmandu: From holy river to unthinkable flowing filth
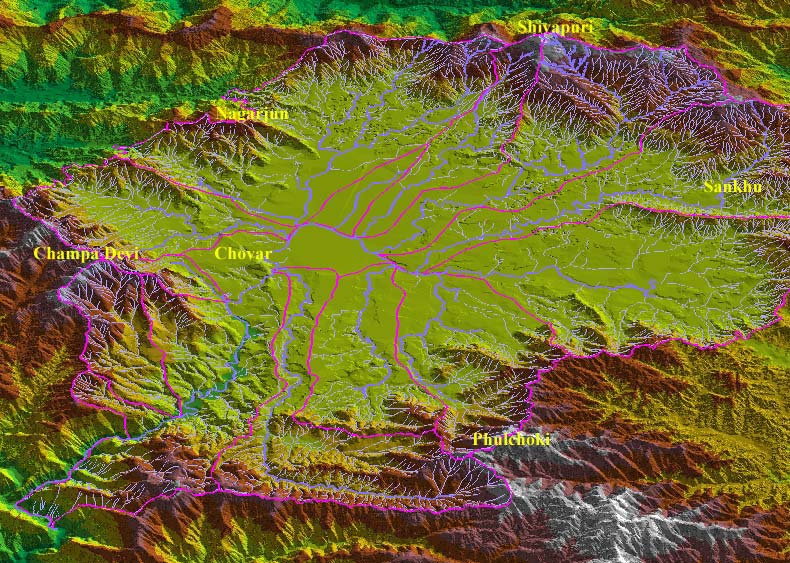
Ajaya Dixit initiated his presentation with a general account of how rivers shape the landscape and how riverine ecosystems have nurtured society and kept civilisations vibrant, cultured and creative. Dixit went on to discuss the basin characteristics of the Bagmati, a tributary of the Kosi that rises in the Shivapuri hills, north of the Kathmandu valley. Around fifteen percent of the basin area (3700 sqkm) lies in Nepal, while the remaining is in India. The average annual rainfall in the basin is 1400 mm and is more than 2000 mm in the hills. Bagmati is a seasonal river with rainfall and springs as its main source. Its mean flow is 15.6 cubic metre/second and low flow is 0.15 cubic metre/second in April.
Kathmandu lies in the Upper Bagmati basin and studies suggest that an ancient lake called the Paleo-Kathmandu lay within the Kathmandu valley as a lacustrine formation. Early settlers lived in lower slopes and used springs and river in the upper reaches. When they moved to the valley floor, they built dongia dharas, which are stone water spouts fed by the unconfined aquifers and delivered water through surface channels. Even today, dongia dharas dated back to 1500 years exist. The state built canals (raj kulo) tapped the upper stretches of the rivers close to the mountains. Rivers and irrigation helped recharge aquifers and ponds.
However, rising urbanisation has damaged these ancient artifacts. Over the last sixty years Kathmandu has expanded massively and its population has increased from 0.41 million in 1951 to 2.6 million in 2011. The city has a huge transient population aside from this, reducing it to a concrete nightmare. Seismologists suggest that Kathmandu is a rubble city in the making. Though the Bagmati river flow has not changed significantly in the last seventy years, the character of the river has been transformed significantly during the period 1970 to 1990. The river has been canalised while the dumping of the city’s garbage into it continues. Dixit identified a plethora of problems faced by the river such as upstream water diversion for drinking water needs, disposal of untreated liquid waste, disposal of solid waste, river jacketing for roads and commercial activities, sand mining and physical encroachment.
The state of the river is an outcome of the current approach to waste management particularly liquid waste management. Three types of waste water namely yellow water flux, grey water and yellow black flux are being generated and flowing water is being used as a vehicle to dispose these. The idea of a water based disposal system e.g. flush toilet embedded in Victorian engineering has led to a technological lock-in with the result that the notion of a natural hydrological cycle has undergone a fundamental transformation.
All the same, the bulk of the load in the river is biological though there are some factories releasing effluents. In the last 20 years some of them have been closed or relocated and the river now stands a chance of being salvaged.

Indus Equation' report by Strategic Foresight Group - Provides clarifications on the water issues between India and Pakistan
Posted on 13 Jul, 2011 04:38 PMWater - Asia's new battleground by Brahma Chellaney: A new book from the Georgetown University Press
Posted on 12 Jul, 2011 01:48 PM The battles of yesterday were fought over land. Those of today are over energy. But the battles of tomorrow may be over water. Nowhere is that danger greater than in water-distressed Asia.
The battles of yesterday were fought over land. Those of today are over energy. But the battles of tomorrow may be over water. Nowhere is that danger greater than in water-distressed Asia.
Himalayan solutions for cooperation and security in river basins : A report by Strategic Foresight Group
Posted on 29 Jun, 2011 07:03 PM This report by the Strategic Foresight Group is a follow-up to its earlier report The Himalayan Challenge: Water Security in Emerging Asia, 2010 . The growing water stress, plans for dams on shared rivers, and uncertainties about the precise impact of climate change have brought water to the forefront of the political agenda of countries in the Himalayan River Basins.
This report by the Strategic Foresight Group is a follow-up to its earlier report The Himalayan Challenge: Water Security in Emerging Asia, 2010 . The growing water stress, plans for dams on shared rivers, and uncertainties about the precise impact of climate change have brought water to the forefront of the political agenda of countries in the Himalayan River Basins.
The report recommends policy options for national governments as well as strategies which can be implemented by local authorities and community groups in a politically viable manner. Some of the ideas may on the surface appear to be addressing micro-level issues. However, such micro-level issues do have an important bearing on security at the macro-level in a large continent such as Asia. This is the experience of many other regions as well, as illustrated in several of the chapters in this report.
The objective of this report is to explore how river basins in the Himalayan region, and particularly shared water resources, can foster cooperation and security between Bangladesh, China, India and Nepal. The conventional view is that depleting water resources, growing problem of pollution, uncertain risks posed by climate change together may lead to competition for resources, migration, social instability, internal conflicts and diplomatic tensions between countries. This view is realistic and was discussed in detail in a previous report of Strategic Foresight Group. It has contributed to spreading the awareness of security risks associated with water crisis in the Himalayan region.
Taking steps toward marine and coastal ecosystem based management: An introductory guide by UNEP
Posted on 25 Jun, 2011 09:28 AMAn important aim of this guide is to facilitate the implementation of UNEP’s overarching Ecosystem Management Programme and new Marine and Coastal Strategy in countries and regions in line with its Medium Term Strategy 2010-13.
"Climate change" - Understanding the connections with energy use, and how India's galloping economic growth and insatiable appetite for energy can be balanced with environmental security?
Posted on 18 Jun, 2011 12:52 AM
Introduction: Energy versus emissions: The big challenge of the new millennium
By Rakesh Kalshian
To maintain its economic growth rate of 8-10%, India needs all the energy it can get. But the momentum of economic growth overrides crucial environmental concerns.
Hotting up: The science and politics of climate change
By Aditi Sen
The world is hotting up. Climate systems are changing. The 1990s were the hottest decade ever, sea levels rose by 10-20 cm during the 20th century, and atmospheric carbon dioxide levels are 31% higher than in 1750.
First-of-its-kind map depicts global forest heights - Update from NASA
Posted on 08 Jun, 2011 10:54 AM European Beech
European Beech
Photo: Forestryimages.org/University of West Hungary/Norbert Frank
Although there are other local-and regional-scale forest canopy maps, the new map is the first that spans the entire globe based on one uniform method.
The work - based on data collected by NASA's ICESat, Terra, and Aqua satellites - should help scientists build an inventory of how much carbon the world’s forests store and how fast that carbon cycles through ecosystems and back into the atmosphere. Michael Lefsky of the Colorado State University described his results in the journal Geophysical Research Letters.
India's forests and REDD+ - A factsheet prepared by Ministry of Environment and Forests
Posted on 28 Apr, 2011 04:29 PMThe benefits of working with REDD and the need and benefits of getting more ambitious by accepting REDD+, which is about finding financial value for carbon stored in standing forests which therefore incentivises the positive elements of conservation is also elaborated here.





