/topics/hydropower
Hydropower
Multi-stakeholder dialogue is messy, but necessary
Posted on 16 Feb, 2012 01:32 PMA workshop on ‘Understanding and resolving water conflicts in the North East India', was organized by Forum for Policy Dialogue on Water Conflicts in India (Forum), in collaboration with Aaranyak (Guwahati), Centre for the Environment, IIT (Guwahati), Arghyam (Bangalore), SaciWATERs-CapNet Network (SCaN) and Cap-Net to discuss emerging issues related to water conflicts and their resolution in the region. This workshop was held in Guwahati on January 23-26, 2012. It aimed at presenting concepts and theory related water conflicts as well as issues especially relevant to the North East Region.
Living rivers, dying rivers: Rivers in the Western Ghats
Posted on 10 Feb, 2012 04:12 PMRiver stories from Maharashtra: Many morals to learn
Parineeta Dandekar’s presentation began with an account of some statistics related to Maharashtra, the third largest state in India. Regarding the state of water resources in Maharashtra, she noted that of the five river basin systems, 55 percent of the dependable yield is available in the four river basins (Krishna, Godavari, Tapi and Narmada) east of the Western Ghats. These four river basins comprise 92 percent of the cultivable land and more than 60 percent of the population in rural areas. 45 percent of the state's water resources are from west flowing rivers which are mainly monsoon specific rivers emanating from the Western Ghats and draining into the Arabian Sea.
With 1821 large dams and more in the offing, Maharashtra has the maximum dams in the country (35.7%). However, the proportion of gross irrigated area vis a vis the gross cropped area at 17.8 percent is much lower than the national average of 44.6 percent. The contradictions from the state, which is home to the highest number of dams, were discussed. In nearly 70 percent of the state’s villages (around 27,600 villages), water is either not available within 500 metres distance, or within 15 metres below ground level or when available is not potable (World Bank, Promoting Agricultural Growth in Maharashtra, Volume 1, 2003).
Dandekar discussed the World Bank funded Maharashtra Water Sector Improvement Project (MWSIP) initiated in 2005 whose main components were establishment, operationalisation and capacity building of Maharashtra Water Resources Regulatory Authority (MWRRA); establishment of river basin agencies in Maharashtra; and restructuring and capacity building of the Water Resources Department. The MWRRA Act (2005) has been amended, taking out the clause for equitable water distribution, and granting the Cabinet the rights to have the last say about water entitlements. This has led to a diversion of water for irrigation from the vulnerable, suicide-prone Vidarbha region to thermal power plants. According to Prayas, “entitlements of more than 1500 MCM have been changed from agriculture to industries and cities”.

Lift irrigation - Methods and practices: A manual by Mihir Maitra (AFPRO)
Posted on 09 Feb, 2012 12:07 PMAccordingly, the book is written as a technical manual that remains accessible to people seeking to gain necessary expertise in the planning, design, installation and maintenance of lift irrigation systems (LIS).
Mining poisons South Goa waters: The case of the Salaulim reservoir shown in a film
Posted on 04 Feb, 2012 05:05 PMContent and Media Courtesy: Video Volunteers
Saving some last remaining free flowing rivers
Posted on 24 Jan, 2012 06:38 AMGuest post by: Parineeta Dandekar
Bangledesh's perspectives on Tipaimukh dam
Posted on 18 Jan, 2012 11:33 PMThe Indian government and two other Indian authorities have signed an agreement on October 22, 2011 regarding construction of the Tipaimukh Dam.
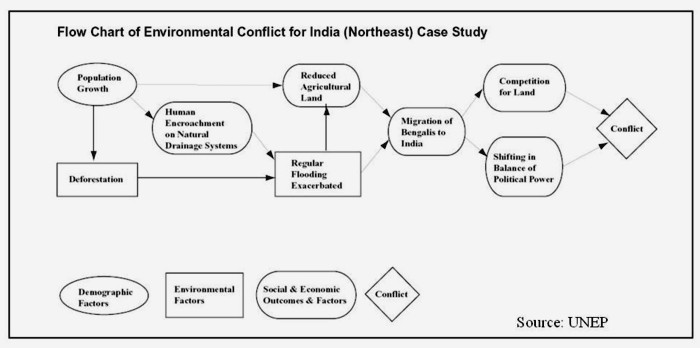
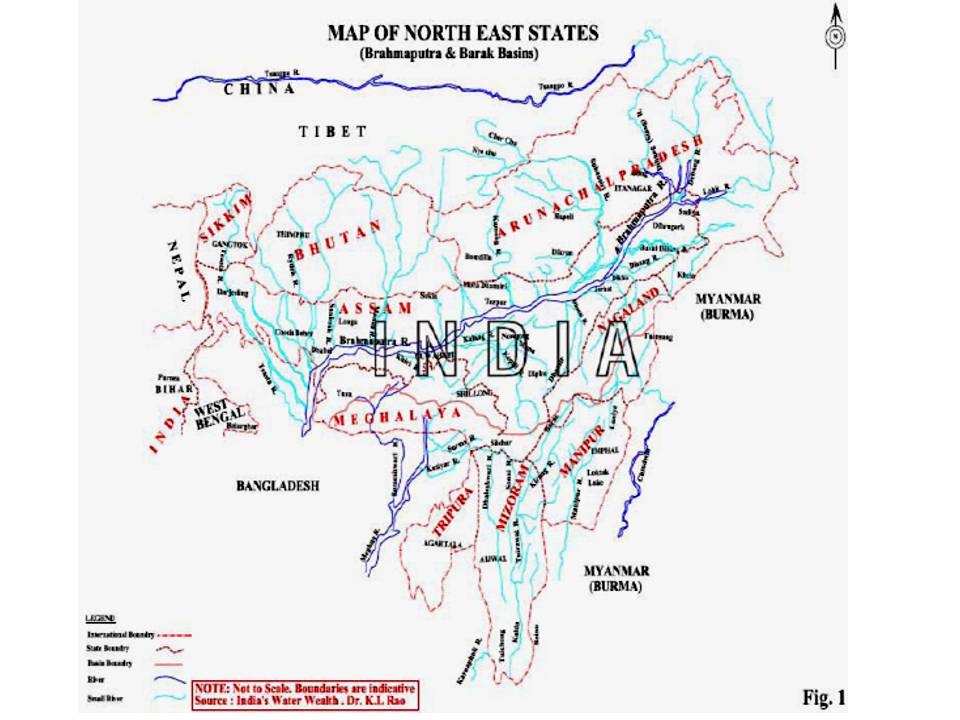
Hydropower in the Northeast: Potential and harnessing analysis - A critique
Posted on 15 Jan, 2012 11:41 PMThe main objectives of the hydropower study are as follows:
- An analysis of the hydropower potential in the Northeast and key elements of the strategy that should be followed for optimal realization of this potential
- An overview of the hydropower development options in the Northeast with regard to the water resources in the different river basins, including consideration of flood control and irrigation
Map of the north-east states
India, Pakistan and water - Lecture by Ramaswamy Iyer at MIDS
Posted on 12 Jan, 2012 10:57 PMIt traces the roots of the conflicts to the strained relations between India and Pakistan following the partition and the framing of the Indus Water Treaty in 1960.
Living rivers, dying rivers: Bagmati river in Nepal
Posted on 05 Jan, 2012 06:07 PMBagmati river in Kathmandu: From holy river to unthinkable flowing filth
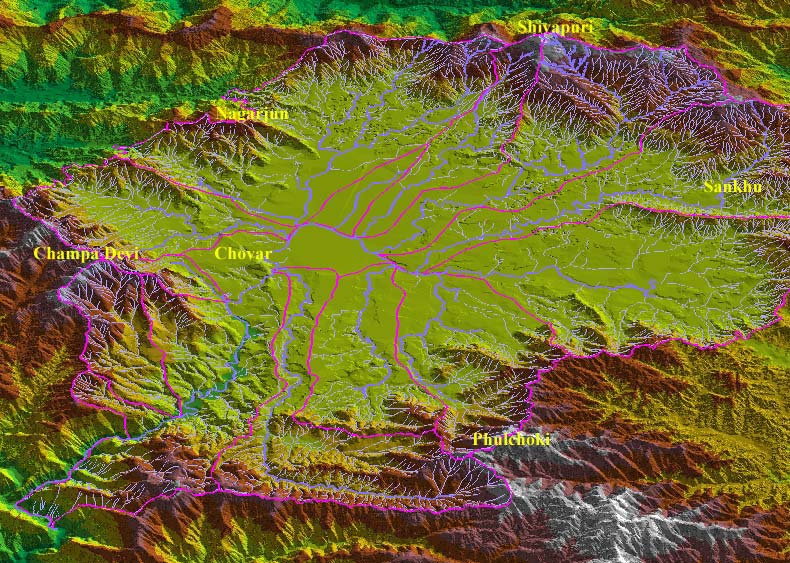
Ajaya Dixit initiated his presentation with a general account of how rivers shape the landscape and how riverine ecosystems have nurtured society and kept civilisations vibrant, cultured and creative. Dixit went on to discuss the basin characteristics of the Bagmati, a tributary of the Kosi that rises in the Shivapuri hills, north of the Kathmandu valley. Around fifteen percent of the basin area (3700 sqkm) lies in Nepal, while the remaining is in India. The average annual rainfall in the basin is 1400 mm and is more than 2000 mm in the hills. Bagmati is a seasonal river with rainfall and springs as its main source. Its mean flow is 15.6 cubic metre/second and low flow is 0.15 cubic metre/second in April.
Kathmandu lies in the Upper Bagmati basin and studies suggest that an ancient lake called the Paleo-Kathmandu lay within the Kathmandu valley as a lacustrine formation. Early settlers lived in lower slopes and used springs and river in the upper reaches. When they moved to the valley floor, they built dongia dharas, which are stone water spouts fed by the unconfined aquifers and delivered water through surface channels. Even today, dongia dharas dated back to 1500 years exist. The state built canals (raj kulo) tapped the upper stretches of the rivers close to the mountains. Rivers and irrigation helped recharge aquifers and ponds.
However, rising urbanisation has damaged these ancient artifacts. Over the last sixty years Kathmandu has expanded massively and its population has increased from 0.41 million in 1951 to 2.6 million in 2011. The city has a huge transient population aside from this, reducing it to a concrete nightmare. Seismologists suggest that Kathmandu is a rubble city in the making. Though the Bagmati river flow has not changed significantly in the last seventy years, the character of the river has been transformed significantly during the period 1970 to 1990. The river has been canalised while the dumping of the city’s garbage into it continues. Dixit identified a plethora of problems faced by the river such as upstream water diversion for drinking water needs, disposal of untreated liquid waste, disposal of solid waste, river jacketing for roads and commercial activities, sand mining and physical encroachment.
The state of the river is an outcome of the current approach to waste management particularly liquid waste management. Three types of waste water namely yellow water flux, grey water and yellow black flux are being generated and flowing water is being used as a vehicle to dispose these. The idea of a water based disposal system e.g. flush toilet embedded in Victorian engineering has led to a technological lock-in with the result that the notion of a natural hydrological cycle has undergone a fundamental transformation.
All the same, the bulk of the load in the river is biological though there are some factories releasing effluents. In the last 20 years some of them have been closed or relocated and the river now stands a chance of being salvaged.

A plan for resolving Mullaperiyar conflict in Kerala - Forum for Policy Dialogue on Water Conflicts in India
Posted on 31 Dec, 2011 12:56 PMGuest Post: Forum for Policy Dialogue on Water Conflicts in India
The Forum for Policy Dialogue on Water Conflicts in India has been closely following the Mullaperiyar issue for the last several years. The polarisation of views around the Mullaperiyar has hardened over the years. The Tamil Nadu government insists that the Mullaperiyar dam is safe and that the water level must be maintained at the maximum level as per the agreement. The Kerala government insists that a new dam, downstream of the present dam, must be built because the present dam is unsafe. The recent tremors with their epicentres near the dam and the already diminishing trust and rising fears and apprehensions on both sides have created a grave situation needing immediate intervention and your initiative in getting the two parties together is a welcome move.





