/sub-categories/information-education-and-communication-campaigns
Information, Education and Communication Campaigns
Transparency demanded in a letter to Jairam Ramesh on Polavaram Project - Himanshu Thakkar
Posted on 04 Sep, 2010 10:43 AM![]()
From:
Himanshu Thakkar
South Asia Network on Dams, Rivers & People,
c/o 86-D, AD block, Shalimar Bagh,
Delhi,
To: Shri Jairam Ramesh
Union Minister of State for Env and Forests (IC), New Delhi
Respected Sir,
I have just seen your letter dated Aug 18, 2010 to Orissa Chief Minister on the aboves subject, uploaded yesterday on MEF website.
- Your letter says that the Forest Clearance has been given to the Polavaram Project on July 28, 2010 is subject to the condition, "... no submergence and displacement of people including STs take place in Orissa and Chhattisgarh...". However, this condition is in complete contradiction with the environment clearance given by your ministry on Oct 25, 2005, which says in para 2, "Total 1,93,35 persons are likely to be affected by this project, out of that 1,75,275 persons in Andhra Pradesh and 6,316 persons from Orissa and 11,766 are from Chattisgarh." It is clear the condition of no submergence and displacement on Orissa and Chhattisgarh, stated in your letter, in the Tribal Development Ministry's condition, and in the forest clearance letter is in complete contradiction with the environment clearance given by you. One of them have to be cancelled due to this contradiction, we would like to know, which one would be cancelled.
Sanitation models in Trichy, Tamil Nadu
Posted on 01 Sep, 2010 04:19 PMA few weeks back I had the opportunity to visit a couple of partners in Tamil Nadu. These two partners are facing a difficult task—sanitation and hygiene implementation through community participation. One project is in the urban slums of Trichy while the other one is a rural project a few hours outside of Trichy. These communities have open defecation rates of 90%. The problem mostly lies on the women. Women feel embarrassed and ashamed to go out in the open, so as a result they only go in the early mornings or late at night—basically during pitch black. Menstrual Health is a topic that is only now being addressed with organizations developing their own branch of sanitary napkin production, sold cheaply to women in rural areas. In addition to the burden on women, open defecation pollutes water sources, thereby leading to diarrhea, one of the biggest killers of children in the developing world.
Restoration of traditional small water bodies in Braj - The South Asian Journal of Tourism and Heritage
Posted on 01 Sep, 2010 02:28 PM This paper published in the South Asian Journal of Tourism and Heritage begins by highlighting the importance of the traditional small water bodies in Braj, commonly known as kunds, as important freshwater sources as well as an important part of the culture and the traditions of the area.
This paper published in the South Asian Journal of Tourism and Heritage begins by highlighting the importance of the traditional small water bodies in Braj, commonly known as kunds, as important freshwater sources as well as an important part of the culture and the traditions of the area.
There were 1000 such kunds, which used to be the source of fresh water in Braj in earlier times. The water was used for multiple purposes like irrigated agriculture, domestic uses, drinking water for cattle, bathing etc. Due to rapid urbanisation, lack of maintenance and prolonged negligence in the last 50-100 years, most of the kunds today have become silted up and are nearing extinction.
The impending crisis for fresh water has forced the planners and policy makers to take cognizance of these traditional water bodies and an urgent need has been identified for taking necessary measures to restore the kunds. The present study thus aims at understanding the reasons for deterioration of the kunds and makes some technical suggestions for revival of these kunds.
Rapid investigations to assess impacts of aquifer recharge - Tumkur district (Karnataka) - A report by ACWADAM and BIRD-K
Posted on 01 Sep, 2010 02:19 PMThis report by ACWADAM is a synopsis of the hydrogeological study carried out for BIRD-K in Pavagada, Sira and Bagepalli areas of Tumkur District, Karnataka. The study aimed at an impact analysis of recharge through borewells as well as suggesting new sites for the same.
The principle objectives of the study were:
- Impact analysis of aquifer recharge through borewells done by BIRD-K in Pavagada and Sira Clusters
- Suggest new sites for aquifer recharge through borewells in Bagepalli cluster.
The methodology used a background study of the area through images from Google Earth. A detailed geological fieldwork in the area was carried out. Various structural and hydrogeological measurements were made to map out the aquifer systems within the area. Water levels in borewells and dug wells were measured. The study area included seven watersheds and falls in two clusters namely Pavagada and Sira. Both these clusters are located in the Tumkur district of Karnataka.
Inspiring progress: Learning from Exnora Green Pammal's solid waste management partnerships in four localities
Posted on 01 Sep, 2010 02:16 PMThis booklet by Exnora Green Pammal (EGP) begins by highlighting the grave situation in relation to solid waste management in the country and the steps undertaken by the government to tackle this issue. The document presents a review of the efforts undertaken by EGP, an NGO based in Chennai, which has been implementing solid waste management projects with a variety of local bodies in accordance with the government’s rules.
India’s solid waste crisis is undermining the nation’s efforts to improve public health, protect the environment and stop climate change. India produces a staggering amount of municipal solid waste every day and the rate of production is expected to climb steadily as the nation becomes more populated, urbanised and economically developed.
Although the Indian government has enacted rules for management and handling of municipal solid waste, the results as per the year 2010 indicate that most localities have not fully complied with the rules and the situation has found to be getting worse day by day. Widespread, prolonged noncompliance with the rules and the rapid, highly-visible environmental degradation has led to calls for a changes in the nation’s waste management policy.
Babhli water conflict: Less water, more politics - EPW article
Posted on 01 Sep, 2010 02:13 PMThis paper published in the Economic and Political Weekly highlights the recently growing conflicts over water sharing between states in India and argues that the intensity and periodicity of these conflicts are increasing and that these conflicts are expected to get worse with the increasing uncertainty of rainfall and water availability. The document goes on to describe the latest one in the news, the conflict between Maharashtra and Andhra Pradesh over the Babhli barrage.
Rainwater harvesting initiatives in Bangalore - A paper by KSCST
Posted on 29 Aug, 2010 12:10 AMThis paper by AR Shivakumar of the Karnataka State Council for Science and Technology (KSCST), presented at a national seminar organised by ISRO at NIAS Bangalore in 2010, begins by highlighting the increasing problem of scarcity of water that the city of Bangalore has been experiencing in recent years and suggests a required plan of action for a sustainable water supply system in the city.
Community organisation in groundwater management – A presentation by ACWADAM
Posted on 27 Aug, 2010 04:01 PM This presentation by ACWADAM on community organization in groundwater management deals with the processes involved in people’s mobilization and participation. The requisites of groundwater management include: resource enhancement, demand management, equitable distribution, institutional mechanism and controlling of free riding. It deals with groundwater management at a local scale when compared to aquifer management.
This presentation by ACWADAM on community organization in groundwater management deals with the processes involved in people’s mobilization and participation. The requisites of groundwater management include: resource enhancement, demand management, equitable distribution, institutional mechanism and controlling of free riding. It deals with groundwater management at a local scale when compared to aquifer management.
Aquifer management involves:
- Identification of aquifer on the basis of geology;
- Identification of recharge and discharge areas;
- Assessment of aquifer capacity and yield through aquifer mapping;
- Protection of recharge area and increasing the groundwater level through artificial recharge in recharge area (based on the geology);
- Treating groundwater as a common property resource;
- Encouraging community use of groundwater and restricting individual use;
- Putting in place an institutional mechanism and legal back up for community groundwater management;
- Awareness generation regarding groundwater and science of hydrogeology.
Hydraulic conductivity: The ability of the rock material to allow the flow of groundwater – A presentation by ACWADAM
Posted on 27 Aug, 2010 08:10 AM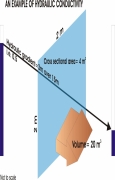 This presentation by ACWADAM on hydraulic conductivity deals with the hydrologic properties of rocks that signify the status of a rock as a good or poor aquifer. The status of a rock with regard to groundwater occurrence and movement is decided by its porosity (specific yield, more practically) and its hydraulic conductivity. These properties decide whether a rock can store and transmit groundwater.
This presentation by ACWADAM on hydraulic conductivity deals with the hydrologic properties of rocks that signify the status of a rock as a good or poor aquifer. The status of a rock with regard to groundwater occurrence and movement is decided by its porosity (specific yield, more practically) and its hydraulic conductivity. These properties decide whether a rock can store and transmit groundwater.
Hydraulic conductivity is also commonly called as permeability of the rock or rock material and is its ability to allow the flow of groundwater through it. A rock with good hydraulic conductivity allows groundwater to easily flow through it.
The presentation describes Darcy’s Apparatus, which comprises of a glass cylinder filled with porous sand. The glass cylinder with the sand bed had an inlet for inflow of water and an outlet for outflow of water. Two vertical glass tubes (manometers) are fitted in the sand tube placed at a fixed distance from each other to measure the respective levels (hydraulic heads).
Karst Hydrogeology – A presentation by ACWADAM
Posted on 27 Aug, 2010 12:42 AMThis presentation by ACWADAM deals with Karst hydrogeology, a term used to denote the topography over limestones, dolomites or gypsum rich rocks where there are sinkholes, caverns and lack of surface streams. Karst mainly refers to carbonate rocks: Limestones (CaCO3) or Dolomites (MgCa[CO]).
The formation of carbonate rocks can be traced to physical and chemical deposition. Physical deposition is clastic in nature formed by deposition of particles carried in suspension. It is marked by higher primary porosity and low secondary porosity. Chemical deposition is in the form of precipitate formed by deposition of particles from solution. Contrary to physical deposition it is marked by low primary porosity and high secondary porosity.
