Author : Ravi Savant
Drinking water can be described as the water intended for human consumption, for drinking and cooking purpose, from any source. It includes water supplied by pipes or any other means for human consumption. Most recently, the UN General Assembly declared access to safe and clean drinking water a human right, essential for full enjoyment of life.
One of the primary goals of WHO and its member states is that
“All the people, whatever their stage of development and their social & economic conditions, have the right to access adequate supply of safe drinking water”
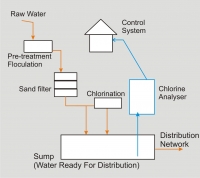
Water treatment methods
Rain water received on earth is in pure form. However, after it reaches on earth, water gets polluted and becomes unsuitable for drinking purpose due to the impurities that are added to it by various means, such as geological structure, Industrial effluents, domestic waste water or chemical fertilizers etc.
Govt. of India has established Indian standard IS:10500 for drinking water, which prescribes limits for various chemical and bacteriological impurities in drinking water. This standard specifies limits for chemical impurities such as hardness, chlorides, fluoride, arsenic, nitrate, iron, turbidity, pH as well as bacteriological impurities such E-coli or thermo tolerant coliform bacteria etc. The agencies that supply drinking water to communities are expected to ensure that the quality of drinking water meets the above standard IS:10500 for drinking water.
Generally, piped drinking water for cities, towns and villages is supplied by local civic bodies such as municipal corporations, zilla parishads or gram panchayats etc. Recently, there is a trend of handing over this job regarding supply of drinking water to private companies.
There are two stages where quality of drinking water is monitored.
- Quality of water at source such as lake, river or dam, etc.
- Quality of water at Municipal water treatment plants where treatment is carried out for purification and supply of drinking water to communities.
Testing of source water is done periodically, once in few months. However, quality of water at municipal water works needs to be checked every day, during treatment of water and before releasing the water for drinking to communities.
In most states, water quality surveillance of source water is carried out in a structure based on a central laboratory, few regional laboratories and basic laboratories located at district levels. This structure is, some times, complemented by staff using portable equipments to make on-site measurements of the most important parameters. Presently, occasional testing of water quality is done, at district level laboratories for samples received from various water sources located in villages & towns in the district. The water samples received from all over the district are sent to district laboratory for analysis.
The most common and widespread health risk associated with drinking water is microbial contamination, the consequences of which mean that monitoring and control of microbial contamination must always be accorded paramount importance to ensure safety of drinking water.
To ensure delivery of safe drinking water in villages and towns, it is necessary to test water there regularly, instead of occasional testing. The local villages or town level laboratories may be augmented with portable chemical test kits and portable microbiological laboratories. These portable kits and portable microbiological laboratories are now commercially available. With the help of the portable microbiological laboratory, regular checking of drinking water for its bacteriological quality can be easily carried out in time locally to ensure safety of drinking water more effectively.
The water received from source such as river, dam or lake etc. is treated at municipal water treatment facilities to remove chemical and bacteriological impurities from it and to make it safe for drinking. There are number of ways of improving quality of water to make it safe for drinking. The most common methods followed at many water works are sedimentation and filtration followed by disinfection.
Typical drinking water treatment methods
Chlorination
Disinfection (killing of harmful organism) of water can be achieved in a number of ways but the most common, is through the addition of chlorine. Chlorine readily dissolves in water and is added to water in the form of chlorine gas or chlorine solution (Sodium hypochlorite). When chlorine is added, it purifies water by destroying the cell structure of organisms.
The disinfection process works effectively only if the chlorine comes in to direct contact with organisms. If the water contains silt (turbidity), the bacteria can hide inside it and not be reached by chlorine. Hence, removing turbidity from water by filtration is an important step in water treatment for effective disinfection by chlorination. The Indian standard IS:10500 specifies a maximum limit of 5 NTU turbidity in drinking water. For on-the-spot, testing of turbidity in the field, handy turbidity scale, which does not require calibration or electricity, is available commercially
Chlorine is a relatively cheap and readily available chemical that, when dissolved in clear water in sufficient quantities, will destroy most disease causing organisms without being a health risk to people. The chlorine, however, is used up in the process as organisms are destroyed. If enough chlorine is added, there will be some left in the water after all the organisms have been destroyed, this is called free chlorine. Free chlorine will remain in the water until it is either lost to the atmosphere or used up destroying new contamination.
Therefore, if we test water and find that there is still some free chlorine left, it proves that most dangerous organisms in the water have been removed and the water is safe to drink. Measuring the chlorine residual in a water supply is a simple and quick method of checking that the water that is being delivered is safe to drink.
The important aspect of residual chlorine testing is that the residual chlorine in water has to be tested immediately on-the-spot, when the sample is drawn. The sample can not be stored and tested after some time because chlorine gets continuously consumed in water and is depleted as time passes. Transport of sample also is not advisable as chlorine gets depleted due to shaking during transport. Hence, for accurate real time results chlorine testing has to be done immediately, on the spot. Field test kits and digital chloro testers suitable for this on-the-spot testing of residual chlorine are available commercially.
IS:10500 for drinking water specifies a minimum limit of 0.2 ppm residual chlorine in drinking water at the consumer end. The residual of minimum 0.2 ppm chlorine at consumer end is required to ensure that the water does not get infected during travel through pipeline from water works to consumer.
In order to ensure that the 0.2ppm residual chlorine is received at consumer end, it is required to maintain the chlorine at slightly higher level before releasing water from water works, so that 0.2 ppm chlorine remains balance even if some chlorine is consumed during travel in pipe line.
It has been observed that clear water requires about 2.0 mg/l chlorine to destroy all organisms with a contact time of 30 minutes. The water will not get completely disinfected if the sufficient chlorine is not added and required residual chlorine (minimum 0.2ppm) is not maintained.
To make sure that the drinking water that reaches the consumer is safe for drinking, it is necessary to check chlorine residual in water very frequently, preferably continuously, at water works during water treatment and before release to consumers.
There are several field test kits for chlorine analysis commercially available. With the help of these kits, on-the-spot testing of residual chlorine can be done in few minutes. Testing with these kits is very economical, simple and does not require much technical knowledge or skill. Hand-held digital chloro testers are also available, commercially.
Chlorotesters

Chlorotesters
These chloro testers are PC compatible and the daily data of chlorine results can be recorded with time and date of testing, and can be stored, downloaded as well as printed.
In the USA, the surface water treatment rules suggest use of online chlorine analyzers for continuous monitoring of residual chlorine on distributed drinking water systems serving more than 3300 people. Variety of chlorine analyzers is now commercially available in India. With the help of these online chlorine analyzers, continuous 24 hours monitoring and control of residual chlorine can easily be done. Making use of this latest technology can help in effectively ensuring safety of drinking water, supplied by the utilities.
In most water works, in practice, this testing of residual chlorine is not done as much frequently as required, for shortage of man power or for various other reasons. At many places, the residual chlorine is monitored only once or twice in a shift, that too only during day shift. During night shift or after office hours it is left to assumption that every thing is going fine by the grace of god.
At one of the water works, where round the clock monitoring was done by online chlorine analyzers on trial basis, it was observed that water released for community consumption during night shifts had zero ppm residual chlorine through out the night.
Online chlorine analyser setup

Online chlorine analyzer
In another town water works facility, it was observed that there was only one person who was assigned with the work of supervision of sedimentation, filtration and chlorination processes along with duties of taking samples for chlorine testing as well as bacteriological testing of drinking water. He was also entrusted with carrying out testing in the laboratory every day, single handed, and maintain the record of testing It is everybody’s guess about safety of drinking water supplied to that town under these circumstances. At such places, water related health disasters are waiting to happen.
The general attitude of people regarding safety of drinking water also needs to be changed. The benefits of good health of the entire community that is accrued due to availability of safe drinking water can not be measured in tangible terms. Cost of avoidance of health disaster, which can happen to entire community due to unsafe drinking water, can also be not measured in tangible terms. We make hue and cry if the municipal water is not received to the taps in the morning. However, mainly we are only concerned about quantity. We are not that concerned about quality. Quality is a most neglected aspect.
At the water works, where it is necessary to augment sampling and testing of chlorine, online chlorine analyzers are useful for monitoring chlorine in water round the clock for 24 hours. With the help of these analyzers it is possible to monitor as well as control dozing of chlorine in water continuously. These analyzers are available in PC, PLC and SCADA compatible versions and automation of chlorine monitoring and dozing is possible with features like SMS alerts for high and low levels of chlorine in water.
It is a well known fact that water borne pathogens enter drinking water system through fecal contamination. This happens when drinking water in pipe lines gets mixed with domestic waste water or industrial effluents etc. By analysis of fecal contamination, we can, therefore, establish whether the water is safe for drinking water or otherwise. As per WHO guidelines, the enumeration of fecal coliform bacteria (thermo tolerant coliform bacteria), which grow at 44 deg C, provide fairly accurate indication regarding bacteriological safety of drinking water.
Portable microbiological laboratory

Portable Microbiological Laboratory
Testing of bacteriological contamination of drinking water, however, also remains a neglected area in public drinking water utilities. It is expected that samples of water from various distribution points are tested regularly for bacteriological contamination. In USA, The Total Coliform Rules (TCR) of Safe Drinking Water Act applies to all public drinking water utilities in USA. The Total coliform rules aims at improving public health by reducing fecal contamination of drinking water. The TCR Rules specify the no. of samples a public drinking water utility should test for bacteriological contamination, every month. As per the rules, the utility, which supplies water to about 1 lakh people, should test minimum 100 nos. samples every month for total coliforms. Utility which supplies drinking water to more than 5 lakh people should test minimum 200 samples every month and so on.
Accordingly, the utilities in India also need to carry out bacteriological testing of water samples from various distribution points regularly. We should not wait for health disasters, such as cholera or other drinking water related epidemic, to happen. This will help them to take quick preventive action, in time. This can be done even without the full-fledged laboratory set up, by using portable microbiological laboratories, which are now available commercially. These portable microbiological laboratories, can be used even by a person with limited skill in microbiology, contains everything required to test for total coliform or fecal coliform bacteria in drinking water samples. These latest techniques can be utilized to ensure provision of safe drinking water.
/articles/strengthening-quality-monitoring-provide-safe-drinking-water-common-treatments-and