This simple guide lists out the most pertinent questions related to watersheds that will help understand this important topic a little better.
Please click on a topic to view more detailed information.
- What is a watershed?
- What is a ridgeline?
- What is the size of a typical watershed?
- Where can one find watersheds? Do I live in a watershed?
- What is the function of a watershed?
- What is land capability classification?
- Why does watershed deterioration occur?
- What are the consequences of a degraded watershed?
- What are the common treatment methods for watershed deterioration?
- What is the system of classification of watersheds in India?
- Is there a code or symbol for the watersheds in the country?
- What does watershed management mean?
- What are the basic objectives of watershed management?
- How are watersheds demarcated?
- What is the role of a wetland in a watershed?
- How many watersheds in the country have been delineated?
- Do my activities impact the watershed I live in?
- Are there any common guidelines for Watershed Development Projects in India?
- What does the 12th Five Year Plan hold for Integrated Watershed Management Programme?
- Any examples of communities that work in watershed protection?
- Any organisations that hold training programmes in watershed management?
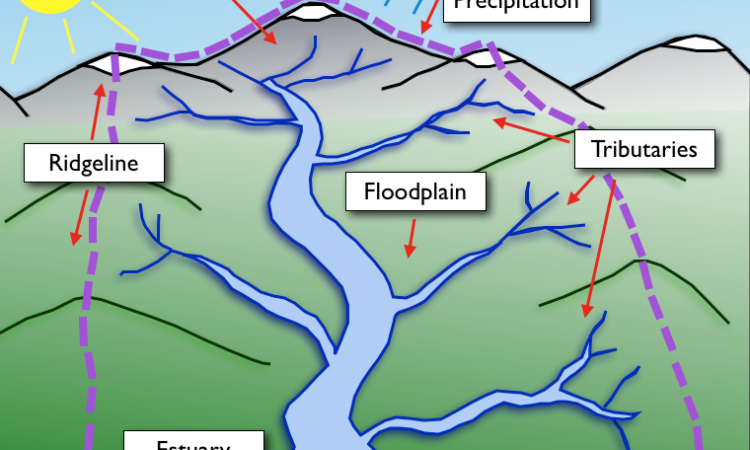
A watershed is the total land and water area, from where the rainfall runoff drains into any water body, be it a stream, river, lake or ocean. It may be a nearly flat area or include hills or mountains.
It is considered to be synonymous with a drainage basin and catchment area. Watersheds are separated from each other and the boundaries are known as watershed boundaries.
What is the size of a typical watershed?
The size of a watershed varies as per the topography of the land. Smaller watersheds drain into streams and just as several streams form a river, several small watersheds group to form a larger watersheds or river basins with their own defined ridgeline.
For an irrigation-cum-hydel project, the size may be several thousands of square kilometers but for a farm pond it could be just a few hectares.
Where can one find watersheds? Do I live in a watershed?
Every land area is a part of some watershed. We can identify our watershed by exploring the water body to which the water from our area drains to. And yes, each one of us lives in a watershed.
What is the function of a watershed?
The main function of a watershed is to receive the incoming precipitation and then dispose it off. It’s five major functions come under the following two heads:
Hydrological functions:
- Collect rainfall water
- Store water in various amounts and for different periods
- Release water as runoff
Ecological Functions:
- Provide conditions and sites for various bio-chemical reactions to take place
- Provide habitat for flora and fauna of various kinds
What is land capability classification?
It is the categorisation of land in watershed management that specifies the land capability. It specifies the ability of the land and indicates the most intensive, profitable, and safe use, which can be made of any piece of land. The land is classified into different capability classes according to various parameters. The broad groups are:
- Land suitable for cultivation: Class I to IV lands
- Land not suitable for cultivation: Class V to VIII lands
Unfortunately, India does not have its own classification system, but uses the USDA system, that has many shortcomings in the Indian context.
Why does watershed deterioration occur?
Watershed deterioration takes place due to uncontrolled, unplanned, and unscientific land use, aided by human interventions. Some of the activities that cause this involve:
- Faulty agricultural methods: Cultivation on sloping land, along nalas and excessive cropping
- Improper management of forestland: Tree felling, thinning of plants on steep slopes, faulty road construction
- Grasslands mismangement: Excessive grazing, development of cattle tracts into channels, compacting soil that results in lower infiltration rates
- Forest fire: Results in loss of vegetation, organic matter
- Shifting cultivation: Destroys protective vegetation, increases soil loss
- Mining and Quarrying: Results in exposure of slopes,destroys vegetation
- Faulty road alignment and construction: Large coarse sediment flow into the drainage channels causing blockage of flow
- Indifference & lack of information amongst people
- Over-burden on land due to population boom
What are the consequences of a degraded watershed?
Some of the results of watershed detioration are:
- Fast running water downhill erodes soils and washes out crops
- Agricultural production reduces
- Increased erosion and denudation of land area within and adjoining the watershed
- Streams get polluted
- Rapid siltation of river beds, reservoirs & water bodies
- Deterioration of water quality due to heavy sedimentation
- Less storage of water, leads to frequent flash floods
- Lowers water table
- Increased incidence of floods and droughts
What are the common treatment methods for watershed deterioration?
- Contour building: Construction of narrow trapezoidal embankments (bunds) along the contours to impound water
- Contour trenching: Excavation of trenches across the slope to break the velocity of runoff, and bunds are created downstream with the material dug out from the trenches
- Contour stone walls: Stones are dry packed across the hill slope to intercept surface runoff
- Bench terraces: Conversion of slopes into level steps fields
- Farm bunds: Constructed on agricultural land, on the contour line, to arrest soil erosion and improve soil moisture profile
What is the system of Classification of Watershed in India?
| Category | Number | Size Ranges (‘000 ha) |
| Regions | 6 | 25000-100000 |
| Basin | 35 | 3000-25000 |
| Catchments | 112 | 1000-3000 |
| Sub-Catchments | 500 | 200-1000 |
| Watersheds | 3237 | 50-200 |
| Sub-Watershed | 12000 | 10-50 |
| Milli-Watershed | 72000 | 1-10 |
| Micro- watershed | 400000 | 0.5-1 |
Is there a code or symbol for the watersheds in the country?
“Watershed Atlas of India” has been devised based on the drainage map on 1:1 million scale following stream hierarchy where the whole country has been divided into six River Resource Regions, 35 Basins, 112 Catchments, 550 Sub-catchments and 3257 Watersheds.
The codification has been made in a simplistic manner following alphanumeric system.
A watershed can be symbolized as 1A2B3 where:
- “1” stands for River Resource Region
- “A” designates the Basin in that river resource region
- “2” indicates the Catchment within the basin
- “B” indicates Sub catchment
- “3” stands for the watershed number in the sequence of stream hierarchy
What does watershed management mean?
Watershed management is simply watershed ‘protection’. It aims to utilize land and water resources wisely, to enable optimum & sustainable production, reduce floods with minimum hazards to natural resources. It essentially relates to the practice of soil and water conservation in the watershed.
What are the basic objectives of watershed management?
The basic objectives are:
- Increase soil infiltration
- Reduce damage caused by excess runoff
- Manage runoff for useful purposes
How are watersheds demarcated ?
Boundary of states, districts, town, farms etc. are demarcated on different maps but watershed is demarcated only on toposheets because these are the only maps, which show the contour lines and the drainage lines. Initially the demarcation of watershed is done on toposheets and then this demarcation can be superimposed on other maps like cadastral maps, soil maps, geological maps etc. It’s demarcation depends on the selected point on the drainage line. Each selected point will have a different watershed boundary and size.
It is the line joining the points of higher elevation in a particular watershed. Ridgeline always divides different watersheds.
What is the role of a wetland in a watershed?
Wetlands are crucial in a watershed, they function as natural water filters and help control and improve the water quality of the water flowing downstream. They provide a conducive atmosphere for many biogeochemical reactions to take place, which help in the removal of nutrients like nitrogen and phosphorus, by converting them from inorganic forms to organic forms. The site of a wetland in a watershed is very important.
How many watersheds in the country have been delineated?
In India, a national level Watershed Atlas has been created. In this Atlas, the entire river systems of the country have been divided into 6 Water Resources Region, which have been further, divided into 35 basins and 112 catchments. These catchments have been further divided into 500 sub-catchments and 3237 watersheds. The atlas consists of 17 sheets on 1:1 million scales along with a compendium of watersheds giving details of other related information such as area within the basin, sharing states and stream names etc.
Do my activities impact the watershed I live in?
What we do affects the watershed we live in, both downstream and for future users. Whether it's doing the laundry, domestic, industrial or agricultural use of water, everyone impacts the watershed they live in. The soaps and detergents that you use, the medicines flushed out, all of these have the potential to affect the water quality in the watershed.
A TMDL (total maximum daily load) is a calculation of the maximum amount of a pollutant that a waterbody can receive and still meet water quality standards.
In other words, it is the sum of the allowable loads of a single pollutant from all contributing point and non-point sources, and includes a margin of safety and consideration of seasonal variations. In addition, a TMDL contains the reductions needed to meet water quality standards and allocates those reductions among the sources in the watershed.
Are there any common guidelines for Watershed Development Projects in India?
Yes there are and these new guidelines for watershed development projects broadly indicate a new framework for the next generation watershed programme. It was asserted that these guidelines coupled with the flexibilities inherent in them, would provide a helpful framework for the design, management and implementation of all watershed development projects in the country. The key features of this new unified approach can be broadly outlined as follows:
- Delegating powers to states
- Financial assistance for institutions
- Duration of the programme
- Livelihood orientation
- Cluster approach
- Scientific planning
- Capacity building
Is Watershed Management Programme mentioned in the 12th Five year plan?
There are new guidelines to Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP) proposed by the Mihir Shah Committee. It has been decided to make the IWMP a five-year programme with a renewed focus on professionalism, capacity building, institutional building and a greater role for civil society. Further, based on the experience of a lot of states, a new framework is proposed for the convergence of IWMP with allied programmes such as MGNREGA and National Rural Livelihood Mission.
Any examples of communities that work in watershed protection?
- Watershed development: Timbaktu
- Self help groups in watershed management: MYRADA
- Participatory watershed management at Ralegan, Ahmadnagar
- Farmer-Participatory Integrated Watershed Management: Adarsha Watershed, Kothapally
Names of organisations that hold training prograames in watershed management?
Some of the organisations that hold training programmes and work in watershed management are:
- ACWADAM
- National Institute of Rural Development
- People's Science Institute.
- WOTR
- Ralegan Siddhi
- NM Sadguru water and development foundation
- Myrada Krishi Vigyan Kendra
- The Barefoot college, Tilonia
- Tarun Bharat Sangh
- International Crops Research Institute For the Semi-Arid Tropics
- WASSAN
References
- Department of Land Resources, GoI
- Watershed Atlas of India
- A source book for soil and water conservation methods
- Integrated Watershed Management Programme (IWMP)
- Watershed Management: Guidelines for Indian Conditions
- The Parthasarathy committee report on watershed programmes in India (2006)
- Micro watershed Atlas of India
- India-WRIS
IWP requests users to view the same as a starting point in collating information on watershed, and to add more suggestions, information as responses in this thread.
Access here: FAQ on watershed
Lead image source: CSERC
/faqs/frequently-asked-questions-faqs-watershed