/topics/groundwater
Groundwater
Arsenic contamination of groundwater in Bihar and mitigation strategies - A research study
Posted on 12 May, 2010 11:24 PM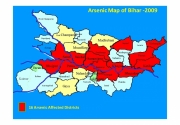 This presentation deals with the problem of arsenic contaminated aquifers in the Gangetic belt of Bihar and the failure of the state government in tackling the crisis and calls for the establishment of a centralized knowledge & research hub with an understanding of the regional peculiarities to mitigate the crisis.
This presentation deals with the problem of arsenic contaminated aquifers in the Gangetic belt of Bihar and the failure of the state government in tackling the crisis and calls for the establishment of a centralized knowledge & research hub with an understanding of the regional peculiarities to mitigate the crisis.
It traces the origin of arsenic crisis to the switch from use of surface water to groundwater. The health impacts of arsenic poisoning and the factors that aggravate arsenicosis are explained. A total of sixteen districts (fifty-seven blocks) in Bihar are affected by high levels of arsenic in groundwater, in trivalent form, which is a more toxic form of arsenic.
Formulating action plan for removal of arsenic contamination in West Bengal - Planning Commission Task Force report
Posted on 12 May, 2010 11:49 AMThe report of the Task Force appointed by the Planning Commission presents an action plan for removal of arsenic contamination in West Bengal. It looks at the extent of the problem, its intake sources, technologies available and the operation and maintenance (O&M) issues.
It outlines the diverse technologies based on various scientific principles, assesses them based on their scale of operation (domestic or community) on techno-economic considerations & infrastructure required and provides suggestions. Short, medium and long term measures are outlined for tackling the problem of arsenic contamination in drinking water supply in the state.
Developing markets for watershed services and improved livelihoods: Fair deals for watershed services in India - An IIED research paper
Posted on 07 May, 2010 10:51 PM The report presents field experiences and lessons in developing Incentive-based Mechanisms (IBMs) for watershed protection services and improved livelihoods at micro and macro-scales, derived from an action-learning project in India at three locations in the states of Himachal Pradesh (HP) and Madhya Pradesh (MP).
The report presents field experiences and lessons in developing Incentive-based Mechanisms (IBMs) for watershed protection services and improved livelihoods at micro and macro-scales, derived from an action-learning project in India at three locations in the states of Himachal Pradesh (HP) and Madhya Pradesh (MP).
An inter-village transaction was facilitated at one site (the Kuhan micro-catchment in HP), while at the second site (Suan micro-catchment in HP) a transaction failed to materialize despite initial interest. At the third site in MP, there was interest in undertaking a transaction between the city of Bhopal and the catchment of its lake, the Bhoj Wetlands.
The action research has yielded insights into the role of hydrological information, types of incentive mechanisms, the importance of institutions and the implementation of IBMs.
Ensuring safe drinking water through innovative technologies to eradicate fluorosis - Sachetana Project - Information manual by BIRDK and Govt of Karnataka
Posted on 05 May, 2010 05:31 PM This manual produced by BIRD-K and DRDPR (GoK) provides the details of the Sachetana project that aims to provide safe drinking water to fluorosis affected populations through the adoption of innovative technologies for rainwater harvesting and groundwater recharge.
This manual produced by BIRD-K and DRDPR (GoK) provides the details of the Sachetana project that aims to provide safe drinking water to fluorosis affected populations through the adoption of innovative technologies for rainwater harvesting and groundwater recharge.
The project is being implemented through the Gram Panchayats of 60 villages from 4 taluks among three districts of Karnataka state over a period of five years (2006-11).
The objectives of the project include:
- Provision of safe drinking water through innovative rain harvesting structures
- Recharge of groundwater through excavation of percolation ponds
- Recharge of existing bore wells and direct recharge of aquifers
- Awareness generation activities to promote sustainable management and management of water resources and water harvesting structures.
Robust watershed modeling options for participative governance - A Water Governance Project review paper
Posted on 30 Apr, 2010 06:01 PMThis technical review paper puts forward robust watershed modeling options as an instrument of participative governance in the water sector, where there is common agreement among stakeholders on assessment of resource and on the manner in which it is to be utilized. Reasonably validated estimates are developed based on existing data and different scenarios are explored. The models offer a scope of assessing the potential changes in watershed hydrology and water availability due to watershed development projects, and can be used as a basis for planning and monitoring.
Capacity Building for Integrated Water Resources Management (Cap-Net) - United Nations Development Programme (UNDP)
Posted on 30 Apr, 2010 11:47 AM![]() Cap-Net is an international network for capacity building in Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM). It includes a partnership of autonomous international, regional and national institutions and networks committed to capacity building in the water sector.
Cap-Net is an international network for capacity building in Integrated Water Resources Management (IWRM). It includes a partnership of autonomous international, regional and national institutions and networks committed to capacity building in the water sector.
The Cap-Net website has a number of resources on water management issues and includes:
Water conservation by Industry – A case study of Mahindra and Mahindra, Zaheerabad
Posted on 30 Apr, 2010 11:07 AMThe presentation deals with Mahindra and Mahindra’s (M&M) work on optimal utilization of groundwater resources in its vehicle manufacturing plant at Zaheerabad, Andhra Pradesh. M&M had taken help from ICRISAT and Groundwater Department of GoAP to study the hydro-geology and topography of the estate and prepare ground water maps.
A time bound master plan of water augmentation was worked out to undertake activities like rainwater harvesting pits, new locations for borewells/ openwells/ percolation tanks, planting of less water intensive trees, re-usage and re-cycling of wastewater, rainwater channels to recharge the under ground water reservoirs and installation of drip irrigation.
Kriti Film Club invites you for the screening of 'The Groundwater Up Project', New Delhi
Posted on 27 Apr, 2010 12:14 PMOrganizers: Tarini Manchanda
Venue: Gulmohar hall, India Habitat Centre, Lodi Road, New Delhi
Description:
Workshop on 'Groundwater for Emergency Situations' (GWES), KIIT University, Bhubaneswar
Posted on 23 Apr, 2010 05:02 PMVenue: KIIT University, Bhubaneswar, ORISSA
Organizer's:
Impact of electricity prices and volumetric water allocation on energy and groundwater demand management
Posted on 22 Apr, 2010 07:53 PMThis paper introduces a theoretical model to examine farmers’ response to changes in power tariff and water allocation regimes vis-a-vis energy and groundwater use. The author begins by explaining the context as one where the existing direct & indirect regulations and direct management interventions have been ineffective in arresting groundwater depletion. Also, there is an absolute paucity of sufficient empirical data to compare and analyze the differential impacts of different levels of pricing of electricity, and groundwater rights allocations on water and energy productivity.
The paper presents a review of farm sector pricing theories and thereafter analyses the potential impact of different modes of electricity pricing on productivity of groundwater use.





