Water is life, essential for daily sustenance and healthy living. With plummeting groundwater levels, contamination of water sources and increasing consumption, challenges in the water sector have increased manifold. Safe, sustainable and affordable water in the face of growing water needs is a severe challenge. With fresh water supplies already hard pressed to meet growing demand, technology plays an important role in managing and using the limited available water in a cost effective and critical manner.
Water contamination occurs both due to human activities and natural processes. Depending upon the purpose for which the water is needed--municipal, industrial or agriculture--treatment is carried out. The technology used will depend upon the current water quality, future standards required and economics of the treatment method. Water treatment removes contaminants that may be biological, physical or chemical in nature.
Various water treatment technologies are present that purify polluted water by removing undesirable chemicals or biological contaminants and making it fit for human consumption. Use based classification of surface waters in India has been laid down by the Central Pollution Control Board (CPCB). The details of the permissible and desirable limits of various parameters in drinking water as per Bureau of Indian Standards (BIS) standard specifications for potable water are also detailed in the IS 10500:1991.
Water treatment plants use technologies to produce water that is safe both chemically and biologically, and that is appealing in terms of colour, odour and taste. The control point for water quality determination must be the consumer's tap and not the treatment facility, which means that the water quality must not be impaired during transmission, storage and distribution to the user. The treatment methods at the plant include aeration, coagulation and flocculation, sedimentation, filtration and disinfection. Some of the prevalent water purification & treatment technologies are listed below.
- Capacitive Deionization (CDI) is a technology where ions are removed from water by passing it through a spacer channel with porous electrodes on each side
- Ozonation is a chemical water treatment technique based on the infusion of ozone into water
- Ultraviolet technology uses Ultraviolet light, just like sunlight, to kill micro-organisms present in the water
- Reverse Osmosis (RO) is a technology that removes a large majority of contaminants by pushing the water under pressure through a semi-permeable membrane
- TERAFIL is a burnt red clay porous media used for filtration & treatment of raw water into clean drinking water, developed Council of Scientific & Industrial Research (CSIR), Bhubaneshwar
- OS- Community scale Arsenic Filter is an organic arsenic filter, developed by IIT Kharagpur
- Filtration methods that may include rapid/ slow sand filters remove dirt, rust, silt, dust and other particulate matter from water
- Solar water purification systems
Water treatment technologies for safe, potable water in rural areas that includes Capacitive Deionization Technology (CDI) using carbon aerogel, solar operated groundwater treatment plants and electro chlorination are described in a booklet ‘Compendium of innovative technologies on rural drinking water & sanitation’ by the Ministry of Drinking Water and Sanitation.
Domestic drinking water filtration methods vary depending upon the method of purification used, the degree of ‘purity’ required, and the type of contaminants in the water. No one technology will fulfil all criteria--there is no ‘silver bullet’ solution. Some of the more popular methods for Household Water Treatment & Safe Storage (HWTS) options includes boiling, SODIS (Solar disinfection), Chlorine Tablets, Liquid Chlorine (online, Biosand filters, Flocculent treatment, Ceramic candle, Filter combinations, Pureit filters, Ultra Violet (UV) filters, Reverse Osmosis (RO) and Ion Exchange (IEX).
For more on water purification systems, click here.
Domestic Greywater Recycling 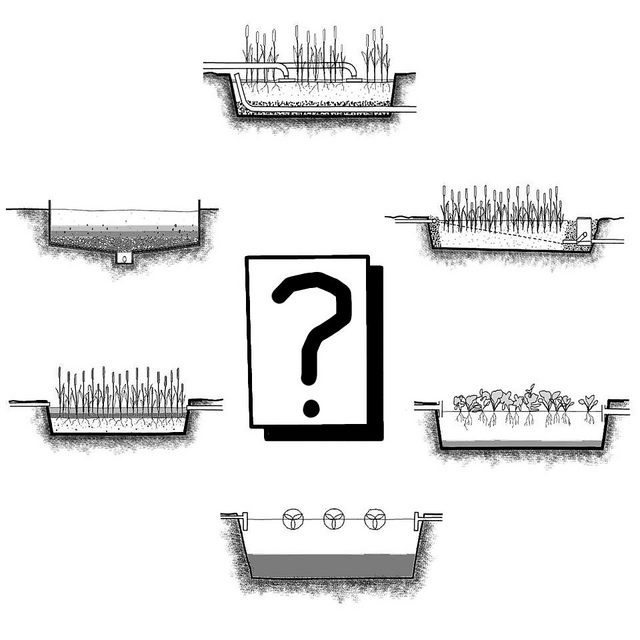
Any used water, other than sewage from toilet basins that exit a house or apartment complex, is referred to as sullage or greywater. This is mostly made up of water used in bathrooms and kitchens, constituting the bulk--nearly 60%-70%--of the total volume of water used in a day.
Before underground sewerage was introduced in most cities, water followed a cyclical route. Water was drawn from dug wells within the premises. Refuse water from the bathrooms and kitchen was let out into the garden while water from the closets reached septic tanks. The soil treated the greywater and sent it back into the ground, thereby closing the household water consumption-reuse loop.
Contrary to popular belief, greywater is largely free from pathogens. As it is mostly made up of easily degradable organic waste and chemicals from cleaning products, it can be purified and reused in-situ with minimal effort. In many homes and apartment complexes, sending this perfectly reusable resource out of the plot along with sewage common-sight. Greywater can be brought back into the water cycle by employing simple biological and mechanical filtration techniques.
There are two basic requirements apart from the necessary plumbing arrangements for treating domestic wastewater:
- Open soil space
- Water loving plants
Water from bathrooms and kitchens can be diverted through a dedicated pipeline into the plant bed set aside for the treatment process. Here, the nutrients present in the waste water are absorbed by water loving plants such as Canna or Cyperus while the soil bacteria polish off the organic waste from the water.
- Constructed wetlands – These wetlands are created to replicate the process of bio-filtration that occurs in a natural setting. Here, the water is purified using two media, the planted surface and the gravel bed underneath.
- Reed bed treatment plants – A smaller version of the constructed wetlands, reed beds are perfect for individual houses and smaller complexes.
- Mechanical filtration – Mechanical systems such as sand filters and pebble flow systems can be used to help filter out waste from the water by separating the discernable solids from the liquid component.
- Lava filters – These pebble filters are a combination of both biological and mechanical systems where the stones act as support structures for microorganisms that help break down the waste.
For more on the basics of rainwater harvesting and greywater recycling, refer Self reliance in water: A book by Indukanth Ragade.
Sewage treatment--Municipal and Industrial
Waste water flowing out of urinals and toilet closets are referred to as ‘blackwater’ or sewage. Blackwater cannot be treated in the same way as greywater as the former contains a heavy pathogen load from the fecal matter suspended in it. Sewage from towns and cities flowing directly into water bodies is one of the major reasons for water pollution.

While City Corporations are in charge of laying underground sewerage pipes to collect, channel and treat sewage, localities outside city limits have a greater responsibility of managing their own waste. Apartment complexes and townships mostly rely on small scale sewage treatment plants (STP) to treat their waste.
Wastewater can be treated either in the presence or absence of oxygen. While aerobic digestion involves the breakdown of waste by microorganisms in the presence of oxygen, anaerobic systems work in its absence. Various types of processes are used to treat both domestic and industrial waste water such as:
- Activated Sludge Process where biological agents such as bacteria are used in the presence of air to oxidise the nutrients present in the sewage
- Sequencing Batch Reactors help equalize, aerate and sediment waste water in timed batches by mixing it with activated sludge and oxygen to reduce the organic load
- Membrane Bio Reactors provide a higher degree of organic and solid removal by combining the principles of both mechanical filtration and biological digestion to treat municipal waste
- Moving Bed Bioreactors are mainly used for aerating and treating high-strength wastewater where several floating polyethylene bio-films move in suspension provide surface area for the nutrient-digesting bacteria to grow
- Trickling filters are low-cost, aerobic systems made up of a fixed bed of gravel, rocks and moss over through sewage is passed to remove the nutrient material in the suspension
- Facultative aerated lagoons are shallow ponds where the sewage is allowed to with the atmospheric oxygen in the upper layers while the sludge settles down at the bottom
- Waste stabilisation ponds, categorized into three broad types – anaerobic, facultative and aeobic depending on the oxygen use intensity – help in reducing nutrient content and polishing waste water to re-use quality
- Up-flow anaerobic sludge blanket digestion treats wastewater in the absence of oxygen where the feed enters the tank through the bottom and flows upward as the bacteria present in the sludge digest organic the matter
The CPCB publication on the status of sewage treatment in India throws light on the performance of sewage treatment plants across the country and the technologies currently being used in them. The status of waste water generation and treatment across the country is also available on the ENVIS Centre on hygiene, sanitation, sewage treatment systems and technology.
/topics/technology






 The practice continues in the country in spite of efforts of several people, implementation of government schemes such as the National Scheme for Liberation and Rehabilitation of Scavengers since 1992 and Self Employment Scheme
The practice continues in the country in spite of efforts of several people, implementation of government schemes such as the National Scheme for Liberation and Rehabilitation of Scavengers since 1992 and Self Employment Scheme