/topics/irrigation
Irrigation
Harvest of water - Watershed programs in Maharashtra make the most of the little rains received
Posted on 02 Nov, 2009 11:23 AMPhotograph by Lynsey Addario
News updates - 15th October, 2009
Posted on 14 Oct, 2009 02:23 PM
Picture from https://www.thehindu.com : (https://www.thehindu.com/2009/10/14/images/2009101451490301.jpg) , drinking water being supplied by tanker in Bellary district
No fresh flood threat:
https://www.thehindu.com/2009/10/13/stories/2009101353490400.htm
Several articles cover the post-mortem of the floods, triggered by CWC statements that their warning to the government of AP was ignored
PIL filed alleging negligence on the part of AP government
Rosaiah reacts:
https://www.thehindu.com/2009/10/14/stories/2009101450460100.htm
https://www.thehindu.com/2009/10/13/stories/2009101359070300.htm
No addition to canal Irrigated areas for 15 years : Report by SANDRP
Posted on 09 Oct, 2009 07:55 PMImage & Content Courtesy: SANDRP
 In fifteen years from 1991-92 to 2006-07 (the latest year for which figures are available), there is been absolutely no addition to net irrigated areas by canals from Major and Medium Irrigation Projects as per official data from the Union Ministry of Agriculture, based on actual field data from states. From April 1991 to March 2007, the country has spent over Rs 130 000 crores on Major and Medium Irrigation Projects with the objective of increasing canal irrigated areas.But the official data shows that this whole expenditure of over Rs 130 000 crore has not led to addition of a single ha in the net irrigated area by canals in the country for the whole of this fifteen year period. In fact the areas irrigated by such projects have reduced by a massive 2.44 million ha during this period.
In fifteen years from 1991-92 to 2006-07 (the latest year for which figures are available), there is been absolutely no addition to net irrigated areas by canals from Major and Medium Irrigation Projects as per official data from the Union Ministry of Agriculture, based on actual field data from states. From April 1991 to March 2007, the country has spent over Rs 130 000 crores on Major and Medium Irrigation Projects with the objective of increasing canal irrigated areas.But the official data shows that this whole expenditure of over Rs 130 000 crore has not led to addition of a single ha in the net irrigated area by canals in the country for the whole of this fifteen year period. In fact the areas irrigated by such projects have reduced by a massive 2.44 million ha during this period.
Water resources in Jhansi and Tikamgarh districts (Madhya Pradesh) - A status report (2007)
Posted on 03 Oct, 2009 05:56 PMThis status report prepared by Development Alternatives contains brief background information about the Bundelkhand region, details about the physical profle (topography, drainage and river systems, land usage, climate, rainfall), water resources information (water demand, availability, supply and accessibility) and information on sanitation practices (toilets, personal hygiene, solid waste management, liquid waste disposal, availability of water for sanitation).
WIO Press Release: Will the wonder irrigation plan take off in Orissa?
Posted on 28 Sep, 2009 05:42 AM- State government promises 5.6 lakh hectares more land under irrigation in the next 5 years.
Irrigation, power and energy resources development in India
Posted on 19 Sep, 2009 03:17 PMAll the above papers and more resources on this subject, are available at this link: http://groups.google.co.in/group/irrigation-power-energy/files?hl=en
Are Pumped Storage Schemes Beneficial For Harnessing The Krishna River Water Further (1995)
Techniques to slow runoff and erosion from steeply sloping land
Posted on 15 Sep, 2009 12:37 PM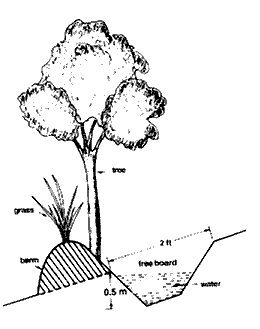 These techniques are useful to slow runoff and erosion from sloping land, and also to revegetate degraded areas. Areas with high rainfall, steep slopes, and thin soils should use slightly graded bunds / terraces / trenches to allow some drainage.
These techniques are useful to slow runoff and erosion from sloping land, and also to revegetate degraded areas. Areas with high rainfall, steep slopes, and thin soils should use slightly graded bunds / terraces / trenches to allow some drainage.
Tips for using bunds in cultivated Land
Posted on 15 Sep, 2009 12:06 PMBunds have many benefits, including marking the boundaries of farm-holdings, slowing the movement of soil and water, and providing a place for integrating trees into agricultural systems. Here are some tips for using bunds within farmland:
- Cattle should be kept away from the area while establishing saplings, by using livehedge fencing. Cactus, Euphorbia spp, and Agave are useful for a livehedge fence.
- Larger trees can be planted on boundary bunds, and smaller trees which will be harvested more frequently can be planted on internal bunds, which divide one holding into separate sections.
How to restore highly degraded lands
Posted on 15 Sep, 2009 11:51 AMIn places where the land is too degraded for agriculture and the soil is too shallow for bunding, rocks can be used to protect existing stumps from browsing and allow regeneration. Rock fences can also be used to protect areas planted with fodder species. Hardy, drought tolerant trees such as neem, tamarind, custard apple, acacia, and eucalyptus can be planted.





