/topics/irrigation
Irrigation
Changes in land use and land cover and establishment of SCS runoff Curve Number in Suddagedda basin – A research report by National Institute of Hydrology
Posted on 24 Jun, 2010 11:52 PMThe study was taken up as a part of the representative basin studies being done by NIH and involved hydrological land use & land cover mapping for the Suddagedda basin of Andhra Pradesh. Mapping was carried out through visual interpretation for the years December 1987, April 1989, December 1992 and November 1996 using IRS IB-LISS II, LANDSAT 5-TM and IRS IC-LISS III data.
Land use and land cover are the most important surface characteristics of a basin. They are very dynamic features over space and time and it is difficult to get real time information on them through conventional means. Planners need to update knowledge of natural resources, which can be obtained quickly, economically and accurately through remote sensing techniques. Further, the land use map of a basin or region provides hydrologically significant categories, which are essential for estimation of reliable runoff from ungauged basins.
Sediment yield estimation for Lower Satluj basin - A research report by National Institute of Hydrology
Posted on 23 Jun, 2010 11:43 PMThe study develops a relationship between suspended sediment load and discharge for three basins - Kasol, Suni and Lower Satluj. The sediment load (tonnes/ year) and sediment yield (tonnes/ sqkm/ year) in suspension and as bed load of sand & gravel through the river channel, reflects upland erosion in the drainage basin and deposition of sediments in the alluvial bottomlands. A good deal of the sediment eroded from upland areas is deposited on lower hills slopes, in bottomlands, lakes and reservoirs.
Bathymetric study of Mansar lake in Udhampur district - A research report by National Institute of Hydrology
Posted on 22 Jun, 2010 08:11 PMThe study undertakes an exhaustive survey of the morphometric features of the Mansar lake, Udhampur district to prepare a bathymetric map of the lake. The map is useful in understanding the lake hydrological behavior through a study of volume, sedimentation rate and identification of the high siltation zone. The study is significant as the lake water can be utilized for drinking and irrigation purposes for the water scarce Kandi belt of Jammu.
Remote sensing and GIS applications in zonation of waterlogging in command areas – A research report by the National Institute of Hydrology
Posted on 21 Jun, 2010 04:48 PMThe study assesses waterlogging in a canal command area in Rohtak and Jhajjhar districts through waterlogging area zonation using multi-spectral and multi-temporal imagery like IRS LISS III data of pre and post monsoon period. Seasonal and permanent waterlogged area and standing water were delineated on the basis of remote sensing data, digital elevation model and groundwater data.
Groundwater quality in adjoining areas of River Yamuna at Delhi - A research report by National Institute of Hydrology
Posted on 21 Jun, 2010 04:41 PMThe study assesses the suitability of groundwater for drinking and irrigation use and examines the likely impact of Yamuna river water quality on groundwater. Delhi is faced with severe problems associated with groundwater quality and quantity. The quality varies spatially and seasonally, with depth and is primarily governed by the extent and composition of dissolved solids present in it. Surface water bodies play a role and the hydraulic gradient determines the lateral and vertical migration in the groundwater flow system.
Groundwater samples were collected through extensive field surveys covering entire Delhi area representing various geo-hydrological and land-use conditions. The data has been analysed with respect to BIS and WHO standards to examine its suitability for various uses. The area has a peculiar feature of infiltration of surface water to groundwater from river Yamuna and from various drains.
Need to bring focus of water & agriculture policies onto rainfed farming : SANDRP May '10
Posted on 18 Jun, 2010 11:03 AM![]()
The Dams, Rivers and People issue for Apr-May 2010 is out. The state government policies, programmes and practices in water resources and highlights the need to bring focus of water & agriculture policies onto rainfed Farming. It is likely to yeild better economic, hydrologic, sustainable, equitable and climate friendly results and foodgrains production as per our future demands.
System of Rice Intensification and Paddy Cultivation - Maps developed by the WWF-ICRISAT Project
Posted on 14 Jun, 2010 06:23 PM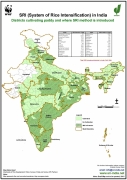 Paddy, one the country's staple crops is cultivated all over the country, barring parts of Jammu and Kashmir, Gujarat and Rajasthan. This set of interesting maps about Paddy and System of Rice Intensification (SRI) from the SRI India website, maintained by the WWF-ICRISAT Project (a joint initiative of WWF and ICRISAT), give a bird's eye view of the districts under Paddy and SRI Paddy cultivation, and the Paddy productivity in various districts of the country.
Paddy, one the country's staple crops is cultivated all over the country, barring parts of Jammu and Kashmir, Gujarat and Rajasthan. This set of interesting maps about Paddy and System of Rice Intensification (SRI) from the SRI India website, maintained by the WWF-ICRISAT Project (a joint initiative of WWF and ICRISAT), give a bird's eye view of the districts under Paddy and SRI Paddy cultivation, and the Paddy productivity in various districts of the country.
Districts with Paddy cultivation and where SRI approach has been introduced: Of the total 604 districts in India, paddy is cultivated in 564 districts. Of these, in 246 districts, SRI paddy cultivation approach has been introduced (data as of 2010). The spread of SRI has been most widespread in Uttarakhand, Eastern Madhya Pradesh, Orissa, Jharkhand, West Bengal, Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu and Karnataka, as 50-95% of the districts in these regions/states have presence of SRI.
Irrigation management transfer in India: The processes and constraints - Paper by IRAP
Posted on 10 Jun, 2010 07:12 PMThe paper discusses the evolution of Participatory Irrigation Management (PIM) in India, following the felt need for better irrigation management to prevent water scarcity in many regions in the country.
The irrigation sector was identified as a priority area in the various policy reforms that took place in the water sector in the country.These reforms emphasised the importance of involving end users/farmers in the operation and management of irrigation conveyance systems.
This led to the establishment of the Farmers Managed Irrigation Systems (FAMIS), which aimed at improving the overall efficiency of the irrigation system, generate a sense of ownership among farmers and to improve the irrigation revenue recovery rate. This laid the seeds for Participatory Irrigation Management (PIM) in India.
Irrigation water management for food security in India: The forgotten realities - Paper by IRAP
Posted on 09 Jun, 2010 06:14 PMIn this paper, the authors examine the current debates around India's water crisis and its implications for food security in the country. The paper takes a critical look at the recent official assessments of groundwater exploitation in India in the context of these debates.
The paper proposes that there is a need to make a qualitative assessment of the magnitude of food security and water management challenges facing the country. It argues that two important factors drive the agricultural growth and food production in India. These include access and availability of arable land and water resources, which need to be examined and analysed with particular reference to their regional variations, to get a true understanding of the situation.
Sustainable Sugarcane Initiative - Improving Sugarcane Cultivation in India - Training Manual developed by WWF India and ICRISAT
Posted on 09 Jun, 2010 01:25 AM Sustainable Sugarcane Initiative (SSI) is an approach to the cultivation of sugarcane, that can reduce inputs - water, chemical fertilizers, seed material and farm space - while improving sugarcane production significantly. It also reduces crop duration and provides a longer period of the cane crushing season to the sugar industry.
Sustainable Sugarcane Initiative (SSI) is an approach to the cultivation of sugarcane, that can reduce inputs - water, chemical fertilizers, seed material and farm space - while improving sugarcane production significantly. It also reduces crop duration and provides a longer period of the cane crushing season to the sugar industry.
This farm-based approach (as opposed to crop-based) also gives farmers options to grow intercrops, such as pulses to improve their income. Most importantly, SSI reduces the overall pressure on water resources and contributes to recovery of ecosystems. It conserves soil moisture, thereby allowing for growing of dryland crops in the same region.
SSI is inspired from the successful approach of System of Rice Intensification (SRI) paddy cultivation, which like SSI, originated from farmers and civil society to improve agricultural productivity while reducing pressure on natural resources.




