/regions/world
World
SIDA invites applications for ISCD programme - Apply by February 3, 2012
Posted on 22 Jan, 2012 10:10 AM![]()
Description:
Half of the Earth’s population is living in coastal areas and the population density here is the double compared to the global average. Coastal zones all over the world are exposed to serious challenges related to over population and to competitive use of resources and ecosystem services from activities such as agriculture, fishery, tourism, urbanisation and industry. Sensitive ecosystems and negative effects from climate change increase the importance of a sustainable development and the need for an integrated planning and management, where the needs and rights of vulnerable groups are taken into account.
6th World Water Forum, World Water Council, Marseille, France, March 12-17, 2012
Posted on 19 Jan, 2012 08:34 PMOrganizer: World Water Council (WWC)
Venue:
The 6th World Water Forum will be held in the "Parc Chanot - Palais des Congrès et des Expositions de Marseille". Located in the 8th District, in the centre of Marseille, a few minutes from the beaches and the Old Port, the Parc Chanot covers 170 000 sqm and comprises a convention centre and an exhibition centre.
India, Pakistan and water - Lecture by Ramaswamy Iyer at MIDS
Posted on 12 Jan, 2012 10:57 PMIt traces the roots of the conflicts to the strained relations between India and Pakistan following the partition and the framing of the Indus Water Treaty in 1960.
Changing currents: Plumbing the rights: A film highlighting water as a common good
Posted on 10 Jan, 2012 08:55 PMSource: Culture Unplugged
Living rivers, dying rivers: Bagmati river in Nepal
Posted on 05 Jan, 2012 06:07 PMBagmati river in Kathmandu: From holy river to unthinkable flowing filth
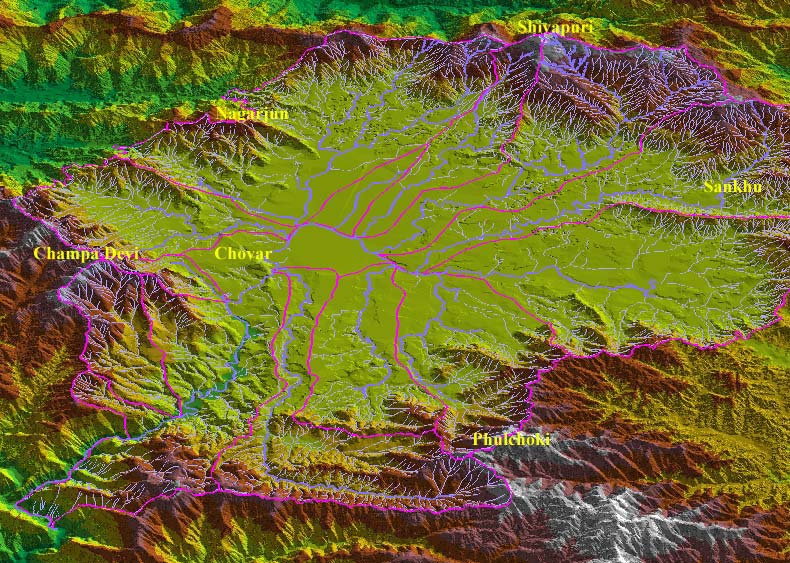
Ajaya Dixit initiated his presentation with a general account of how rivers shape the landscape and how riverine ecosystems have nurtured society and kept civilisations vibrant, cultured and creative. Dixit went on to discuss the basin characteristics of the Bagmati, a tributary of the Kosi that rises in the Shivapuri hills, north of the Kathmandu valley. Around fifteen percent of the basin area (3700 sqkm) lies in Nepal, while the remaining is in India. The average annual rainfall in the basin is 1400 mm and is more than 2000 mm in the hills. Bagmati is a seasonal river with rainfall and springs as its main source. Its mean flow is 15.6 cubic metre/second and low flow is 0.15 cubic metre/second in April.
Kathmandu lies in the Upper Bagmati basin and studies suggest that an ancient lake called the Paleo-Kathmandu lay within the Kathmandu valley as a lacustrine formation. Early settlers lived in lower slopes and used springs and river in the upper reaches. When they moved to the valley floor, they built dongia dharas, which are stone water spouts fed by the unconfined aquifers and delivered water through surface channels. Even today, dongia dharas dated back to 1500 years exist. The state built canals (raj kulo) tapped the upper stretches of the rivers close to the mountains. Rivers and irrigation helped recharge aquifers and ponds.
However, rising urbanisation has damaged these ancient artifacts. Over the last sixty years Kathmandu has expanded massively and its population has increased from 0.41 million in 1951 to 2.6 million in 2011. The city has a huge transient population aside from this, reducing it to a concrete nightmare. Seismologists suggest that Kathmandu is a rubble city in the making. Though the Bagmati river flow has not changed significantly in the last seventy years, the character of the river has been transformed significantly during the period 1970 to 1990. The river has been canalised while the dumping of the city’s garbage into it continues. Dixit identified a plethora of problems faced by the river such as upstream water diversion for drinking water needs, disposal of untreated liquid waste, disposal of solid waste, river jacketing for roads and commercial activities, sand mining and physical encroachment.
The state of the river is an outcome of the current approach to waste management particularly liquid waste management. Three types of waste water namely yellow water flux, grey water and yellow black flux are being generated and flowing water is being used as a vehicle to dispose these. The idea of a water based disposal system e.g. flush toilet embedded in Victorian engineering has led to a technological lock-in with the result that the notion of a natural hydrological cycle has undergone a fundamental transformation.
All the same, the bulk of the load in the river is biological though there are some factories releasing effluents. In the last 20 years some of them have been closed or relocated and the river now stands a chance of being salvaged.

Unaglobal Consult & Marketing calls for EoI from paddy farmers in India to support farmers in Nigeria - Apply by January 8, 2012
Posted on 02 Jan, 2012 03:32 PMUnaglobal is a consulting firm that sources and markets commodities. It was established to service its clients for import, export and investment activities in the Imo state of Nigeria, under the umbrella organisation of Imo State Investment Promotion Agency (ISIPA).
World Bank Group invites applications for Junior Professional Associate in Water Anchor-World Bank – Apply by January 2, 2012
Posted on 27 Dec, 2011 08:24 AMContent courtesy: Winrock Water
![]()
The World Bank is a vital source of financial and technical assistance to developing countries around the world. Its mission is to fight poverty with passion and professionalism for lasting results and to help people help themselves and their environment by providing resources, sharing knowledge, building capacity and forging partnerships in the public and private sectors. The Water Anchor is a unit within the Transport, Water and ICT Department of the Sustainable Development Vice-Presidency of the World Bank Group. The Water Anchor integrates all water disciplines, including: agricultural water management, water supply and sanitation, water resources management, hydropower, and water quality and environment.
Strengthening rural livelihoods – A report by IDRC
Posted on 13 Dec, 2011 05:17 PM This report prepared by International Development Research Centre (IDRC) examines how information related constraints in poor rural areas are being overcome and how information technology is being employed to the benefit of people in South Asia.
This report prepared by International Development Research Centre (IDRC) examines how information related constraints in poor rural areas are being overcome and how information technology is being employed to the benefit of people in South Asia.
Poor people are constrained by limited access to information and poor communications technology. The research looked at the use of ‘information communications technologies’ (ICTs) in providing agricultural extension services, getting timely market price information, finding out about rural wage labour opportunities, helping rural communities to build a sustainable asset base and understanding crop diseases and soil nutrition.
The results of the research bring together rigorously tested practices and methods of applying ICTs for improving rural livelihoods. Each research study has investigated how and to what extent a specific ICT intervention made a difference. Together it shows how ICTs have empowered rural people and transformed livelihoods in agriculture: by filling information gaps, raising awareness, building skills and extending social networks.
The focus was on agricultural communities, as Asia’s poor and middle-income countries have primarily agriculture-based economies. However, a broader ‘livelihoods’ approach has been taken to ensure that we observe the variety of ways ICTs can have an effect on rural communities. The scope of the research took into account the range of on-farm and off-farm productive and reproductive activities that support farming households and communities.
A river runs through us: An award-winning film on the threats faced by our rivers
Posted on 18 Nov, 2011 03:32 PMArticle and media courtesy: International Rivers
PSIPW invites applications for 5th Prince Sultan Bin Abdulaziz international prize for water, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia - Apply by January 31, 2012
Posted on 15 Nov, 2011 09:34 AMContent courtesy: Fundforngos

Prince Sultan Bin Abdulaziz International Prize for Water (PSIPW) aims to give recognition to the efforts that scientists, inventors and research organizations around the world are making in water related fields.