/regions/rivers
Rivers
Basin-level impact assessment study of the Lohit river - A study by WAPCOS & Ministry of Environment and Forests (2011)
Posted on 19 Mar, 2012 11:29 AM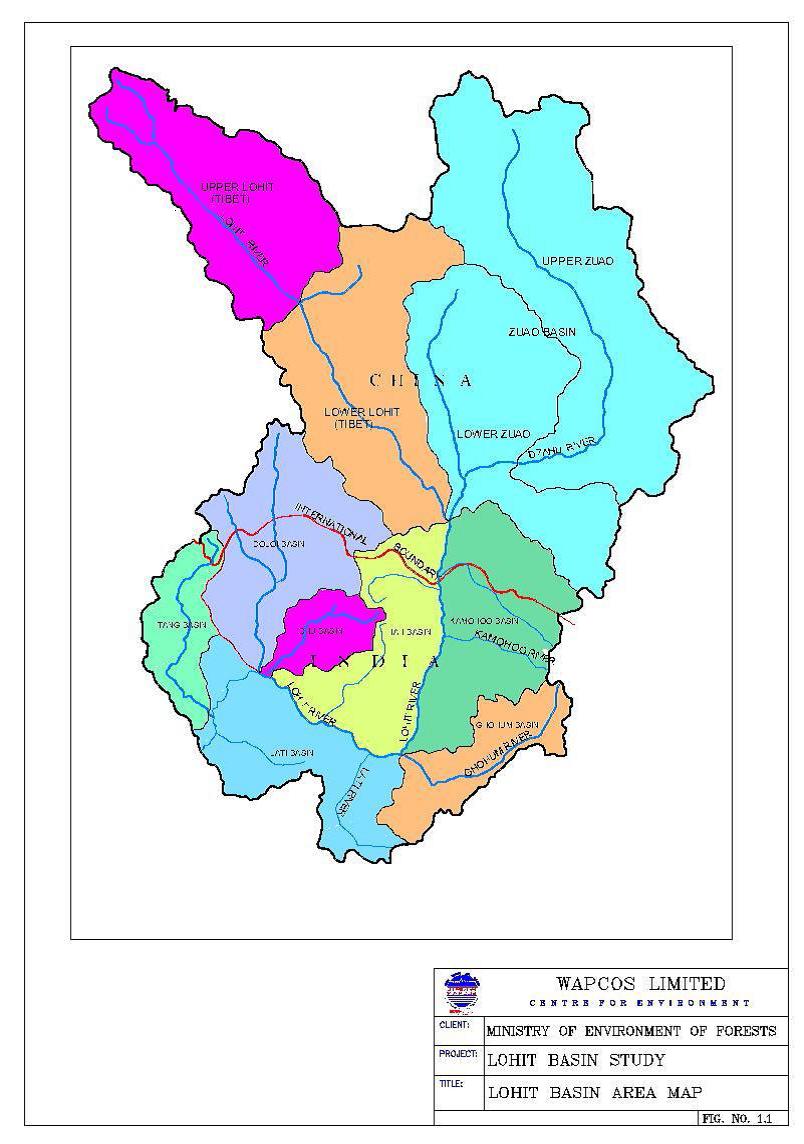
Bore well recharging through "V" wire technology in Belavadi village, Chikmagalur district in Karnataka
Posted on 12 Mar, 2012 07:02 PMVideo Courtesy : FLRWHS
Ignoring precaution, MoEF clears a project which has been categorically rejected by majority Standing Committee of the NBWL
Posted on 26 Feb, 2012 01:31 PMGuest Post : Parineeta Dandekar and Himanshu Thakkar
The status of glaciers in the Hindu Kush-Himalayan region - A report by the ICIMOD
Posted on 17 Feb, 2012 03:00 PMThe HKH region is one of the most dynamic, fragile, and complex mountain systems in the world as a result of tectonic activity and the rich diversity of climates, hydrology, and ecology. The high Himalayan region is the freshwater tower of South Asia and has the highest concentration of snow and glaciers outside the polar regions giving it the name Third Pole.
Balati glacier, Pithoragarh district, Uttarakhand (Source: Uttarakhand and I)
"Understanding and resolving water conflicts in the North East": Workshop held at Guwahati, 23-26 January 2012
Posted on 16 Feb, 2012 01:31 PMGuest post by: Raju Mimi
Living rivers, dying rivers: Rivers in the Western Ghats
Posted on 10 Feb, 2012 04:12 PMRiver stories from Maharashtra: Many morals to learn
Parineeta Dandekar’s presentation began with an account of some statistics related to Maharashtra, the third largest state in India. Regarding the state of water resources in Maharashtra, she noted that of the five river basin systems, 55 percent of the dependable yield is available in the four river basins (Krishna, Godavari, Tapi and Narmada) east of the Western Ghats. These four river basins comprise 92 percent of the cultivable land and more than 60 percent of the population in rural areas. 45 percent of the state's water resources are from west flowing rivers which are mainly monsoon specific rivers emanating from the Western Ghats and draining into the Arabian Sea.
With 1821 large dams and more in the offing, Maharashtra has the maximum dams in the country (35.7%). However, the proportion of gross irrigated area vis a vis the gross cropped area at 17.8 percent is much lower than the national average of 44.6 percent. The contradictions from the state, which is home to the highest number of dams, were discussed. In nearly 70 percent of the state’s villages (around 27,600 villages), water is either not available within 500 metres distance, or within 15 metres below ground level or when available is not potable (World Bank, Promoting Agricultural Growth in Maharashtra, Volume 1, 2003).
Dandekar discussed the World Bank funded Maharashtra Water Sector Improvement Project (MWSIP) initiated in 2005 whose main components were establishment, operationalisation and capacity building of Maharashtra Water Resources Regulatory Authority (MWRRA); establishment of river basin agencies in Maharashtra; and restructuring and capacity building of the Water Resources Department. The MWRRA Act (2005) has been amended, taking out the clause for equitable water distribution, and granting the Cabinet the rights to have the last say about water entitlements. This has led to a diversion of water for irrigation from the vulnerable, suicide-prone Vidarbha region to thermal power plants. According to Prayas, “entitlements of more than 1500 MCM have been changed from agriculture to industries and cities”.

Governing the urban poor - Riverfront development, slum resettlement and the politics of inclusion in Ahmedabad - A paper published in EPW
Posted on 08 Feb, 2012 11:58 AMSabarmati Riverfront Development (SRD) project, an urban mega-project in Ahmedabad has been proclaimed as a case based on “flexible governing” of the residents of the riverfront informal settlements.
River basin planning for Ganga : Lessons from Murray-Darling Basin Authority
Posted on 02 Feb, 2012 09:15 PMThis interactive session with NGOs working on water and river issues was held in continuation of the “Living rivers, dying rivers” series at the request of AusAid. The meeting was chaired by Prof. Ramaswamy R. Iyer, Honorary Professor, Centre for Policy Research and an author of books and articles on water while the lead speaker Dr.
Saving some last remaining free flowing rivers
Posted on 24 Jan, 2012 06:38 AMGuest post by: Parineeta Dandekar
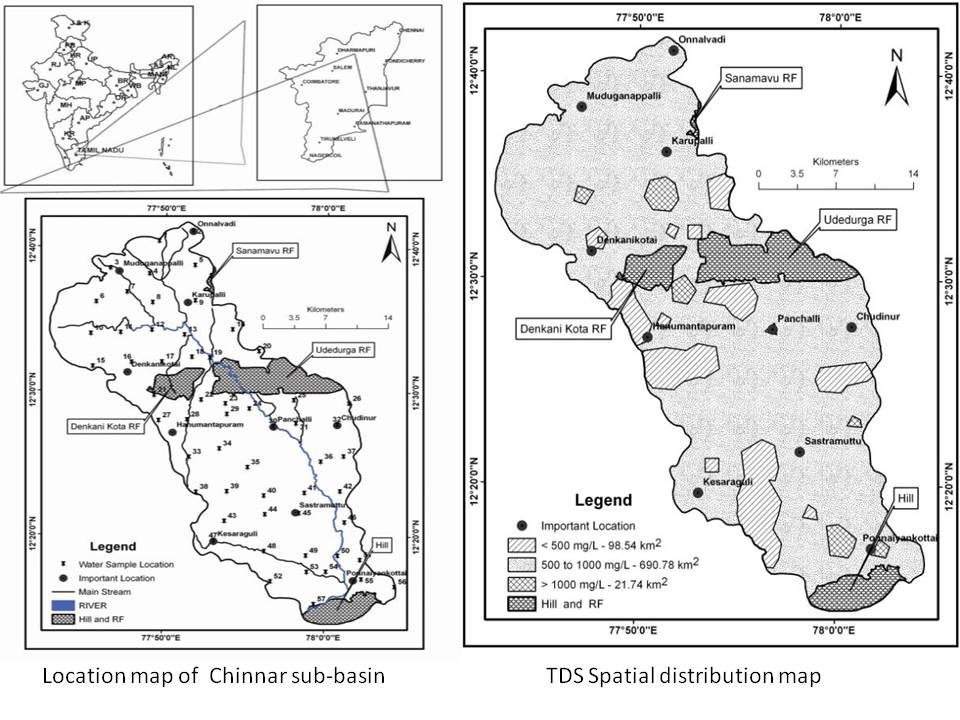
Evaluation of physico-chemical characteristics in groundwater using GIS – A case study of Chinnar sub-basin, Cauvery River, Tamil Nadu, India
Posted on 20 Jan, 2012 04:26 PMThe study found that the groundwater of the basin is extremely hard with total hardness, magnesium and potassium contents being above the permissible limits. Thirty nine out of 57 samples exceed the allowable limits for fluoride.