/regions/bay-bengal
Bay of Bengal
On the brink: Water governance in the Yamuna river basin in Haryana
Posted on 08 Dec, 2010 10:07 PMThis study attempts to develop a case study of the Western Yamuna Canal Command in Haryana with the purpose of developing a general picture of the institutional environment and arrangements related to water resource development and use in the State of Haryana. It is based on a review of water law, policy and administration and helps draw conclusions on whether the existing governance systems are meeting the current needs and suggests alternate options. The study has attempted to test the following hypothesis –
Palak Dil Lake - Mizoram
Posted on 26 Nov, 2010 03:00 PMThe Mizoram state has three types of (natural) lakes: valley lakes, tectonic/landslide lakes and artificial reservoirs, but the only lake of significance is Palak Dil, which is a natural lake in a depression in the hills. Palak Dil may possibly be a combination of valley and tectonic lakes. Locally in Mizoram, lakes are called dils. There are many such dils scattered all over the state, but they are tiny pools or marshy depressions such as Rengdil, Tamdil and Mampui Dil (Choudhury 2002). The Palak Lake is situated within the Mara Autonomous district Council, which is a region inhabited by the Mara Tribe. The Maras are distinct from the majority Mizos and in the Mara language the Palak Lake is referred to as Pala Tipa.
Urban local initiatives and government responses: A case of Dev Nadi in Pune
Posted on 21 Oct, 2010 01:26 PMMost of the rivers and streams in urban India are dead. With a very few and rare exceptions, these once-beautiful water bodies have been encroached upon, sources dried up or converted into sewage drains all over the country.Water is being sourced or pumped from sites upstream of the city for its needs or from long distances and the city administration has little incentive for cleaning its own muck. The dismal figures of urban sewage treated by sewage treatment plants, their installed capacity and efficiency stand testimony to this.
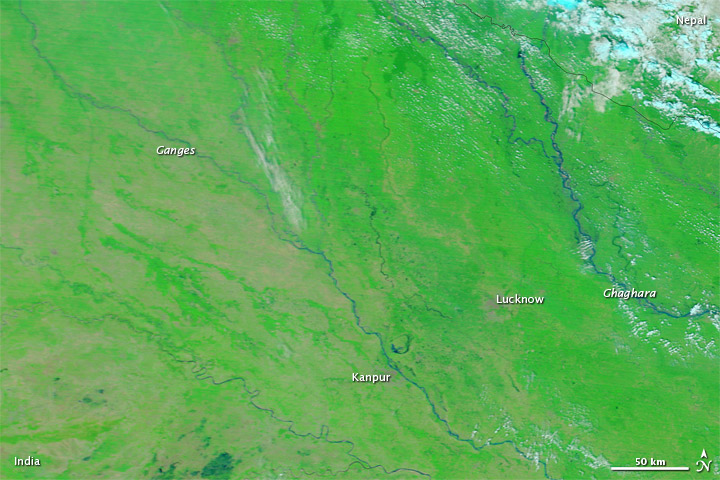
Flooding in Northern India: Updates from Earth Observatory
Posted on 28 Sep, 2010 02:16 PMHeavy monsoon rains had pushed the Ganges and other rivers over their banks by late September 2010. The flooding left at least 2 million people homeless in northern India, Reuters reported. Some 500,000 hectares (1.25 million acres) of agricultural land were also flooded. Authorities reported that the Ganges and its tributaries had risen to near record levels, and meteorologists forecast more rains in the days ahead.
The myth of flood controls - A note by Dinesh Kumar Mishra
Posted on 18 Sep, 2010 04:41 PMIn the light of the recent major floods in river Yamuna, the enclosed article that deals with the question and futility of man made structures like dams and embankments to control floods may be found useful.
But it is unfortunate that even this otherwise very insightful article does not reflect anywhere on the fact that the floods in monsoon months are natural events and should be acknowledged and planned for accordingly.
There is a need to better understand the phenomenon of floods and not to treat them as some kind of natural calamity requiring artificial man made safeguards.
It may be noted that Dr D K Mishra who has studied the floods in river Kosi for decades has been making these points for many years now. It is necessary to heed to people like him if we do not wish to invite more trouble in future.
Dr G.D. Agrawal s tapasya - Achieved the desired result
Posted on 30 Aug, 2010 12:47 PMDr G.D. Agrawal’s tapasya, his third fast-unto-death, has finally achieved the desired result. Since 2008, Dr Agrawal has been trying to persuade the Government of Uttarakhand and the Government of India that R. (Bhagirathi) Ganga must be allowed to flow in its natural state in the uppermost reach between Gangotri and Uttarkashi. The two governments had plans to construct three new large hydropower projects in this stretch. Dr Agrawal’s fasts have led to the scrapping of all the three projects.
Environmental flows in river basins: A case study of river Bhadra - Current Science
Posted on 26 Aug, 2010 12:50 PMThe quantity and seasonality of water flow in a river may greatly change from its normal condition between a major storage and downstream, thus paving the way for drastic changes in the riverine ecosystem. ‘Environmental flow’ refers to the amount of water considered sufficient for protecting the structure and function of an ecosystem and its dependent species.
The paper goes on to describe the case of river Bhadra, which is the site of a dam that has significantly altered the natural flow of the river and describes the study that aimed at conducting the environment flow analysis of the river.
Groundwater externalities of surface irrigation transfers under national river linking project: Polavaram – Vijayawada link
Posted on 25 Aug, 2010 05:00 PMThis document published by IWMI and CGIAR describes the details of the Polavaram project, which has been planned by the state of Andhra Pradesh as a multi-purpose project:
- to provide irrigation benefits to the upland areas
- to provide a water supply to the industries in Visakhapatnam city, including the Steel Plant, for the generation of hydropower
- for the development of navigation and recreation facilities.
The project envisages the construction of an earth-cum-rock filled dam that is 1,600 m long across the Godavari River at Polavaram, and about 42 km upstream of the Godavari Barrage at Dowlaiswaram.
Salvaging and scapegoating: Slum evictions on Chennai’s waterways - EPW paper
Posted on 02 Aug, 2010 01:03 AMThe paper highlights the case of recent projects that have been planned on the river Cooum in Chennai.
The encroaching Ganga and social conflicts: The case of West Bengal
Posted on 01 Aug, 2010 01:39 AMThis report deals with the social conflicts emerging out of the encroachments owing to the change in course of the Ganga upstream and downstream of the Farakka barrage. The barrage was built with the intention of diverting water into the Hugli river with a view to flush the sediment load into the deeper part of the estuary and revive the navigational status of Kolkata port. During the last three decades of its operation, the silt-management in the barrage was given scant or no attention. The sediment movement in the tidal estuary of Hugli is a function of a complex fluvial system that can hardly be governed by inducing 40000 cusec of water.