
Rainwater harvesting (RWH) is a simple method by which rainfall is collected for future usage. The collected rainwater may be stored, utilised in different ways or directly used for recharge purposes. With depleting groundwater levels and fluctuating climate conditions, RWH can go a long way to help mitigate these effects. Capturing the rainwater can help recharge local aquifers, reduce urban flooding and most importantly ensure water availability in water-scarce zones. Though the term seems to have picked up greater visibility in the last few years, it was, and is even today, a traditional practice followed in rural India. Some ancient rainwater harvesting methods followed in India include madakas, ahar pynes, surangas, taankas and many more.
This water conservation method can be easily practiced in individual homes, apartments, parks, offices and temples too, across the world. Farmers have recharged their dry borewells, created water banks in drought areas, greened their farms, increased sustainability of their water resources and even created a river. Technical know how for the rooftop RWH with direct storage can be availed for better implementation. RWH An effective method in water scarce times, it is also an easily doable practice. Practical advice is available in books written by Indukanth Ragade & Shree Padre, talks by Anupam Mishra and other easy to follow fun ways.
Read our FAQ on Rainwater Harvesting and have many basic questions answered.
/topics/rainwater-harvesting






 This
This 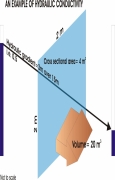 This presentation by
This presentation by 
